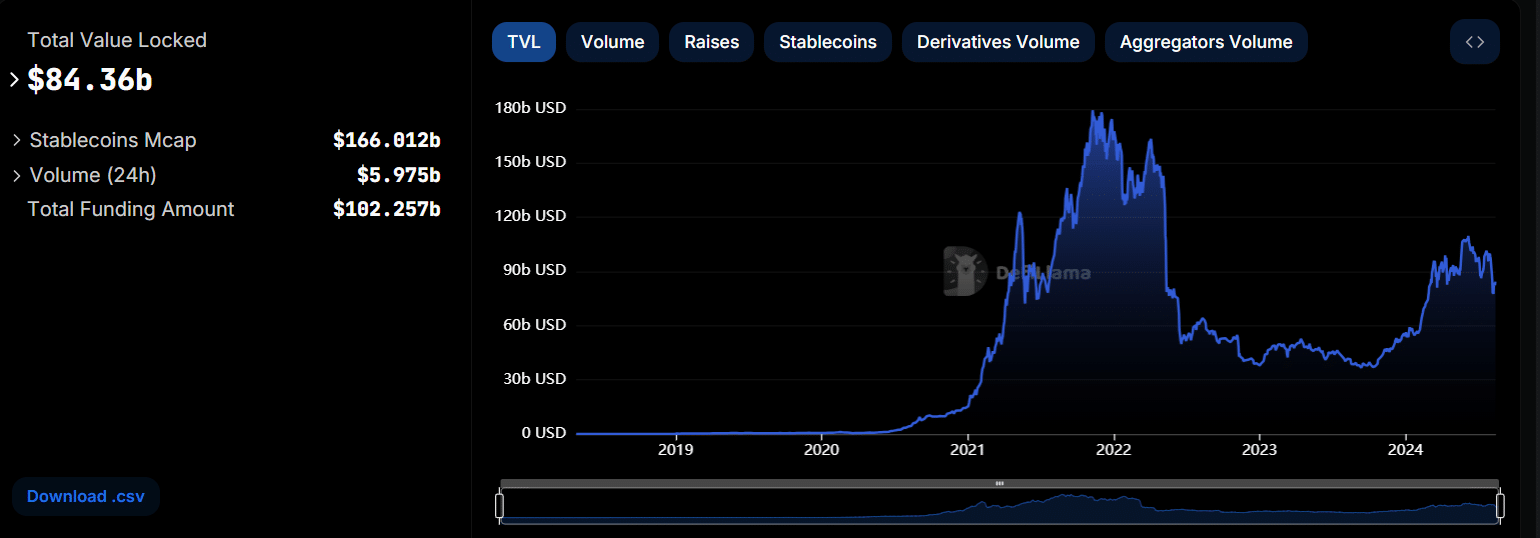
TradFi refers to traditional finance organizations; CeFi refers to centralized crypto businesses; DeFi refers to decentralized crypto platforms.
Written by: Anatol Antonovici | Updated August 9, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace

In 2024, investors can choose from a range of financial products and platforms built upon different infrastructures. In this article, we’ll discuss the three main ‘Fi’s’: traditional finance (TradFi), centralized finance (CeFi), and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
-
TradFi is the conventional, old-school financial system that relies on intermediaries like banks, market makers, stock and bond markets, and insurance companies. This system operates with fiat money and traditional assets, including securities, commodities, and real estate.
-
CeFi shares similarities with TradFi in terms of approach as it also relies on centralized intermediaries. However, this ecosystem operates with blockchain-based cryptocurrencies, which governments do not issue. CeFi is considered ‘off-chain’.
-
DeFi is an emerging financial infrastructure powered by blockchain technology and operates exclusively with digital assets. Instead of intermediaries, the rules in DeFi are enforced by smart contracts. DeFi is considered ‘on-chain’
What Is TradFi?
Traditional finance (TradFi) is the conventional financial system that has been around since the birth of civilization. TradFi markets are heavily regulated by governments and institutions, e.g., central banks and financial watchdogs.
The main players in TradFi are intermediaries like banks, stock exchanges, payment operators, and insurance companies. These intermediaries dictate the rules based on the regulatory framework that differs from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
TradFi encompasses the world’s largest markets, including foreign exchange (forex), real estate, equities, commodities, and derivatives.
📚 Read: Traditional finance jumping into crypto is bringing confidence – Financial Times
How Does TradFi Work?
While TradFi has adopted many digital solutions, it is still centralized, with the balance sheets, order books, and transactions being controlled by centralized entities.
There are few peer-to-peer (P2P) interactions in TradFi. Instead, most transactions are managed by intermediaries, with users being forced to trust them and share control over their funds and assets.
Also, intermediaries dictate the rules according to regulations. For example, banks rely on the fractional reserve system that enables them to lend way more than they hold as deposits.
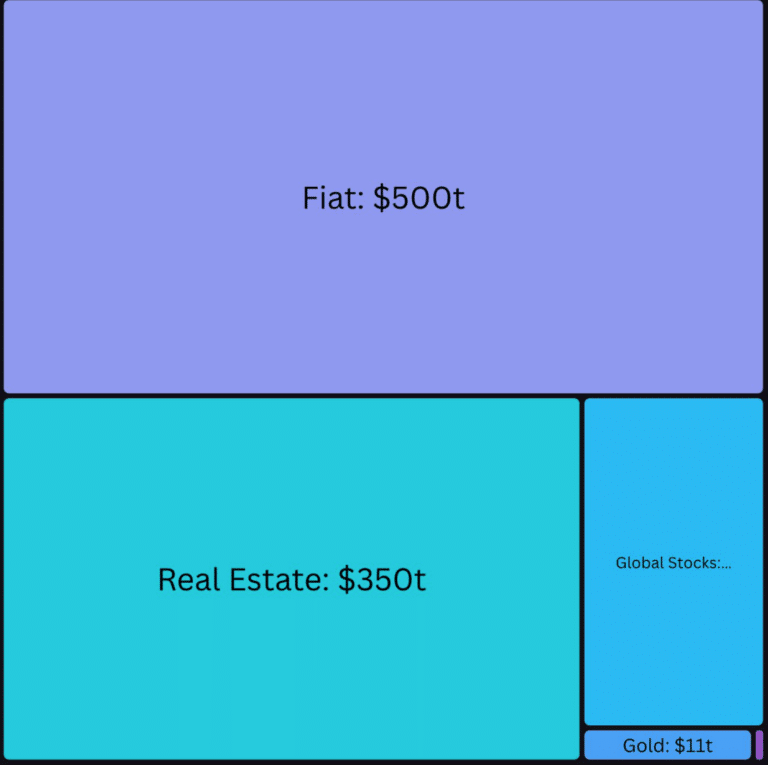
The below image shows the largest asset classes in existence. Note the size of the fiat currency market compared to that of crypto (which is the tiny purple dash at the bottom right!).
What is CeFi?
Centralized finance (CeFi) is a relatively new market born from the need to address the growing demand for cryptocurrency interactions. Satoshi Nakamoto launched Bitcoin in 2009 as a decentralized money system hosted on the first version of a blockchain.
Shortly after Bitcoin gained traction, developers and entrepreneurs started to build more advanced blockchain platforms, with thousands of utility tokens popping up over the years. The crypto market almost hit $3 trillion at its peak.
While Bitcoin and most altcoins are decentralized at the core level, the need to exchange these digital assets led to the appearance of centralized exchanges – the first use of CeFi.
In order to access blockchain in its truest form, you need a self-custody crypto wallet. Unfortunately, self-custody wallets can be complicated for those who are not tech-savvy. Also, if you lose the ‘seed phrase’ (also called a recovery phrase) to your wallet, there is no way to recover your funds.
CeFi simplifies this process by holding the private keys of its users, which can be good and bad (think FTX!).
Today, centralized finance comprises all kinds of centralized financial services built around cryptocurrencies. It offers use cases like trading, lending, saving, custody, cross-chain, stablecoins, insurance, asset management, and other applications.
📚 Read! Private Key vs Seed Phrase vs Recovery Phrase: Crypto 101
How Does CeFi Work?
Like TradFi, CeFi services are managed by centralized intermediaries, e.g., exchange platforms like Binance. Kraken, Gemini & Coinbase. Some cryptocurrencies, especially stablecoins, are issued by centralized entities that are pegged to an underlying asset, mainly the US dollar. For instance, Circle issues USDC while Tether is behind USDT.
Basically, CeFi is a simulation of TradFi aimed at digital assets instead of fiat and real-world assets. This means that users have to trust crypto service providers and often give up crypto ownership by holding the funds in hot wallets hosted by exchanges.
Besides facilitating crypto-to-crypto transactions, CeFi offers fiat on- and off-ramps to bridge the gap between the crypto industry and traditional finance. This helps traders better manage their positions when volatility is high.
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) remain the dominant use case in CeFi and the entire crypto market, with their daily volume ranging from tens to hundreds of billions, as shown by Coinmarketcap data.
📚 Read: CEX vs DEX – Crypto Exchange Fees Comparison
What is DeFi?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging trend with the goal of building on the promise of decentralization. The distinctive aspect of financial decentraliazed applications (dApps) is that they enable users to access crypto services without intermediaries. DeFi protocols represent trustless financial systems where the conditions and settlements are managed by smart contracts. DeFi is about building financial services on blockchain infrastructures to cut middlemen and transfer control from centralized entities to communities.
DeFi exploded in 2020 and is likely here to stay. Bank of America and ING have concluded that DeFi was more disruptive than the mighty Bitcoin.
The best way to measure the size of the DeFiecosystem is to monitor the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi applications, which refers to the crypto locked as collateral. As of August 2024, the TVL figure hovers near $84 billion. It peaked in 2021 at over $210 billion.
How Does DeFi Work?
DeFi applications are run by smart contracts and are decentralized to the point where even governance is in the hands of communities through so-called Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
Many times, however, a centralized entity still influences a community. For example, Uniswap Laps is the centralized entity primarily responsible for Uniswap. Over time, DeFi apps try to decentralize control through actions such as the release of governance tokens.
The most popular use cases in DeFi are decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending apps.
Unlike CEXs, DEXs enable traders to swap tokens simply by connecting their self-custody wallets. There are no intermediaries involved. The conventional order book is eliminated. Instead, the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model is used.
AMMs operate liquidity pools representing pairs of tokens where liquidity providers lock crypto in exchange for rewards from trading fees.
Lending protocols enable lenders to earn interest by locking crypto. On the other side, borrowers can access crypto funds without any credit score and KYC, although they should be ready for over-collateralization.
Ethereum is the predominant blockchain behind DeFi as this network can store transactions AND code, while Bitcoin can only store code. The native currency of Ethereum is ether (ETH). In order to transact on Ethereum, you need to pay network fees called gas fees.
DeFi Activities
Other DeFi activities include:
TradFi vs CeFi vs DeFi: What Do They Offer?
CeFi acts as a mediator between TradFi and DeFi, with the latter seeking to empower communities and eliminate intermediaries altogether. CeFi may overlap with TradFi wherever fiat is involved.
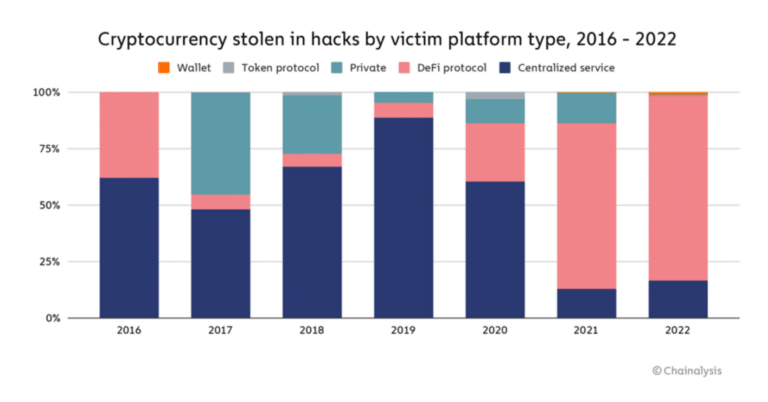
Despite the benefits of DeFi, TradFi is still more comfortable for the masses due to user-friendly UX and strict regulation. Regarding regulations, DeFi is still the wild west, while CeFi is in an ongoing transition to become recognized by governments. According to Chainalysis, 2022 was a record year for crypto hackers, and DeFi accounted for most losses.
Nevertheless, DeFi is at a nascent phase and holds a lot of promise. If DeFi manages to improve user experience and address security issues, the trend may explode in the coming years.
FAQs
The differences between the three have to do with the existence of intermediaries and the level of control from communities. Unlike the first two, DeFi requires no middlemen, with the rules being enforced by smart contracts. Users interact with DeFi apps in a non-custodial manner with no KYC required.
Also, DeFi operates exclusively with digital assets, while TradFi exclusively with fiat and traditional assets. Nevertheless, DeFi might be exposed to TradFi through stablecoins and synthetic assets.
TradFi, CeFi, and DeFi can offer the same use cases, such as trading, lending, and asset management. Also, CeFi and DeFi operate with cryptocurrencies. In fact, CeFi and DeFi aim to solve the same problems by using different means.
It really depends on your needs. TradFi is ubiquitous and is the go-to place for everyday transactions, such as payments, transfers, and credits. The exposure to CeFi and DeFi opens the door to a new world of opportunities, such as margin trading and yield farming. For crypto fans seeking to build lucrative portfolios, it’s best to consider a diversified approach.
Additional Reading:
What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and How Does It Work? – Investopedia
What is CeFi? Centralized Finance on Blockchain – Blockchain Council

Anatol Antonovici
6+ years of experience writing for crypto brands and blockchain firms, including Coindesk, Cointelegraph, Bitcoinist, CryptoPotato, Algorand, and OTCTrade.com
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences