Lyra Finance’s (now Derive) revolutionary automated market maker (AMM) technology makes it the most popular DeFi options protocol in Web3.
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated September 5, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows
In June of 2024, Derive is the most popular DeFi options protocol in existence. In this article, I’ll pull from my 15 years of experience in the options markets to show you how this revolutionary options trading platform matches up liquidity providers with option traders.
🍒 tasty takeaways
Derive is the most popular decentralized finance (DeFi) options protocol in June of 2024.
The Derive Protocol is a permissionless protocol that settles perpetual and options trades.
- The protocol is deployed on an Optimistic Rollup that settles to the Ethereum blockchain
The Derive Protocol is governed by the Derive DAO and DRV token holders.
Users can connect their self-custody crypto wallets to the Derive protocol to trade options and become liquidity providers, earning fees from trading activity.
Lyra Finance Summary
| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| Derive | Derivatives infrastructurethat facilitates critical yield, hedging, and price discovery functions all across the crypto ecosystem. |
| Automated Market Makers | Users provide liquidity in decentralized exchange pools earning fees from trading activities. |
| How Derive Works | Connects to self-custody crypto wallets, allowing trade on options after bridging to supported Layer 2 blockchains. |
| Derive MMVs | MMVs hedge their delta exposure using Arbitrum or Optimism, offsetting risks in options trading. |
| Liquidity Providers | Anyone can deposit cryptocurrencies to earn a percentage of trading fees from MMVs. |
| Derive Ecosystem | Polynomial, Toros, DeDeLand, Kwenta, Brahma, and dHedge leverage Lyra's technology. |
What is Derive?

Derive is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that makes markets (provides liquidity) in decentralized options contracts with automated market maker (AMM) technology.
Derive can be broken down into four segments:
The Derive Chain
Derive Protocol
Derive Interface
Derive Governance
In this article, we are going to focus on the Derive interface, which of course includes the Derive protocol.
Note: Derive is currently not available to US citizens, but this will hopefully change soon.
🏃 Let’s go!
What Are Automated Market Makers (AMMs)?
AMMs like Uniswap are the backbone of DeFi. Users that wish to buy or sell crypto in DeFi connect to a decentralized exchange (DEX) and tap into whatever liquidity pool they are trading.
For example, if you want to buy ETH and sell USDC, you would access the ETH/USDC pool, which is stored on a smart contract.
So who provides the crypto in these pools that you are trading from? Anyone. You could be a ‘liquidity provider’. All you have to do is deposit an equal value of two cryptocurrencies into a liquidity pool. As traders trade from this pool, you earn fees!
📚 Read: Liquidity Pools for Beginners
The AMM model is in contrast to TradFi, which employs order books and market makers (Citadel, Virtu) to provide liquidity.
Derive: An AMM for Options
Derive takes the Uniswap AMM model and tweaks it for options trading.
However, making markets in options is much more complicated than making markets in spot crypto, like Uniswap.
This is because options are derivatives: their prices are contingent upon a separate underlying asset.
Because of this, options are incredibly sensitive to many things. In options trading, these sensitivities are divided into the four ‘Greeks’.
Delta: How much crypto do the options represent at any given time?
Theta: How fast does the option decay over time?
Gamma: At what rate does the Delta change?
Vega: How sensitive is the option to changes in the underlying volatility?
Derive is one of the first DeFi protocols to price options almost as well as traditional market makers – which have much more versatility. They’re not there yet, but they’re getting closer with every upgrade.
How Does Derive Work?
To trade options on Derive, you will need to first connect your self-custody crypto wallet to the protocol.
Derive supports Ethereum and five layer 2 blockchains, including:
Arbitrum
Optimism
Base
Blast
Mode
📕 Read: Arbitrum vs Optimism vs Polygon
⚠️ In June of 2024, Lyra supports only ether (ETH) and bitcoin (BTC) options.
Derive: Selecting a Strike Price
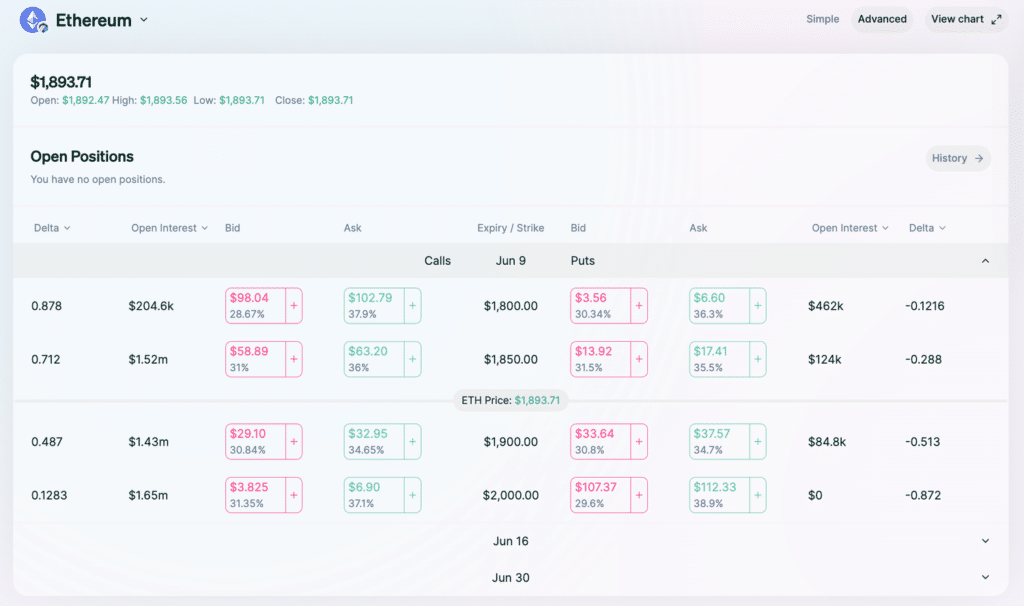
After you are connected to the Lyra interface you can choose to trade either call options or put options.
As a reminder, call options are leveraged bullish bets on the underlying while put options are leveraged bearish bets.
📈 Need a refresher course on options? Check tastylive’s out here!
After you have chosen an option to buy (or sell), you need to select the way in which you will be paying/ putting up collateral for that option. Derive currently accepts two stablecoins and three crypto assets:
USDC
USDT
ETH
wstETH
WBTC
Note: Derive allows options traders to sell (go short) options on a partly collateralized basis.
Derive Market Making Vaults (MMVs)
So you have placed your trade. The less inquisitive mind may be content to leave it at that. But in DeFi, ignorance is NOT bliss, so let’s see what happens under the hood at Derive.
Options trading is a risky business. Whenever you buy an option, a party is on the other side selling you that option. Being short call options is not a very pleasant experience as the loss is unlimited.
The process of offsetting this risk in options trading is called ‘delta hedging’. If you are buying an option with 90 delta, the market maker needs to offset that risk by selling 90 delta.
According to the Derive website, this protocol’s MMVs hedge their delta exposure in two different ways depending on the Layer 2 being used:
Arbitrum: By opening a long or short perpetual forward position at GMX
Optimism: Creating a spot synth position on Synthetix
But where do the funds come from to buy and sell these synths and perpetual?
From liquidity providers.
Let’s learn about ‘LPs’ at Derive next.
Note: In order to hedge an option, you have to price an option. Derive uses the Black-Scholes model to price options. On this page, Lyra goes into more detail about how they price their options.
Lyra Liquidity Providers
Anyone can be a liquidity provider on Derive. As users trade from the MMVs, you earn a percentage of their trading fees.
In order to be an LP at Derive, you must first deposit one of two different cryptocurrencies.
USDC
sUSD
Once your crypto is in an MMV, it can be redeemed at any time (following a short waiting period).
Providing liquidity for Derive does come with risks:

Derive has measures in place to protect LPs against two major risks:
Delta Risk (changes in the underlying)
Vega Risk (implied volatility changes)
To learn how Derive mitigates these risks, check out this video from Greg at AD Derivatives.
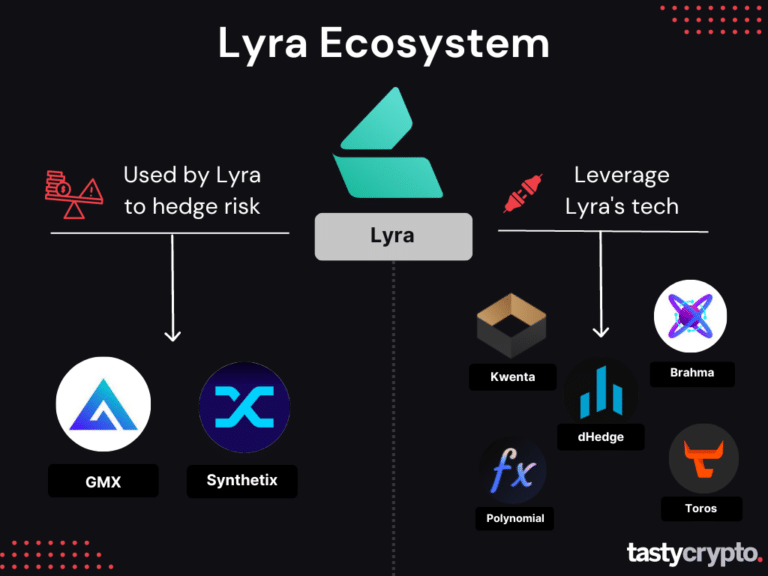
Derive Ecosystem
Derive FAQs
‘LYRA’ was the native governance token of the LYRA network, but migrates to LDX, which will launch in the third quarter of 2024. Lyra has a TVL (total value locked) of $58 million.
Derive has proven to be a safe and user-friendly platform to trade the decentralized options market. However, currently, both liquidity and trading volume have fallen from their peaks.
Derive runs on Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, Blast, and Mode.
Yes, Derive is an open-source DeFi project.
Many different DeFi options protocols leverage Lyra’s technology.
Polynomial: Options vaults
Toros: Options vaults
DeDeLand: Options and perpetual trading
Kwenta: Options and perpetual trading
Brahma: Uses Lyra for leverage and hedging risk
dHedge: Digital asset management platform integrated with Lyra
Read Next: EigenLayer Explained
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences


Mike Martin
Mike Martin formerly served as the Head of Content for tastycrypto. Before joining tastycrypto, Michael worked in the active trader divisions of thinkorswim, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. He also served as a writer and editor for projectfinance.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.

