Curious about Ethereum and Ethereum ETFs? This blog will break down these key differences, helping you make informed investment decisions.
Written by: Anatol Antonovici | Updated August 5, 2024
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace
Whether you’re a crypto veteran or a newcomer, understanding Ethereum vs. Ethereum ETFs can enhance your investment strategy.
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
Ethereum ETFs enable traditional investors to gain exposure to the second-largest cryptocurrency. How do they differ from holding physical Ether?
- The US SEC approved Ethereum ETFs at the end of July 2024.
- As of this writing, investors can choose from nine Ethereum ETFs.
Ethereum ETFs are traded in the form of shares listed on traditional stock exchanges.
Summary
| Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Ethereum | Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Its native cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH). |
| Ethereum ETF | An Ethereum ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund) is a financial product that allows investors to gain exposure to Ethereum without directly buying the cryptocurrency. It trades on traditional stock exchanges and aims to mirror the performance of Ethereum's price. |
What Are Ethereum ETFs?
Ethereum spot exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment funds that provide investors with direct exposure to Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap.
Ethereum ETFs are listed on US stock markets and can be purchased in the form of shares, similar to those of public companies.
In January 2024, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) finally approved the first batch of spot Bitcoin ETFs, bringing tens of billions from institutional and retail investors. Seven months later, on July 22, it was Ethereum’s turn to receive the green light from the regulator, which approved nine ETFs. Trading started the next day.
Spot Ethereum ETFs are backed by physical Ether coins held by issuers, enabling investors to gain exposure to Ethereum through traditional brokerage platforms.
🍒 Bitcoin vs. Bitcoin ETFs
What Ethereum ETFs Are Available for Trade?
The SEC approved nine application filings from Grayscale, BlackRock, Bitwise, Fidelity, and 21shares, among others. Here is the full list of Ether ETFs with their tickers:
While Bitcoin (BTC) is regarded as a store of value (SoV) asset, often nicknamed digital gold, Ethereum (ETH) powers a fast-growing ecosystem of decentralized applications (dapps) thanks to its smart contract feature. Spot Ether ETFs provide institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) with indirect exposure to blockchain sectors such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and Web3.
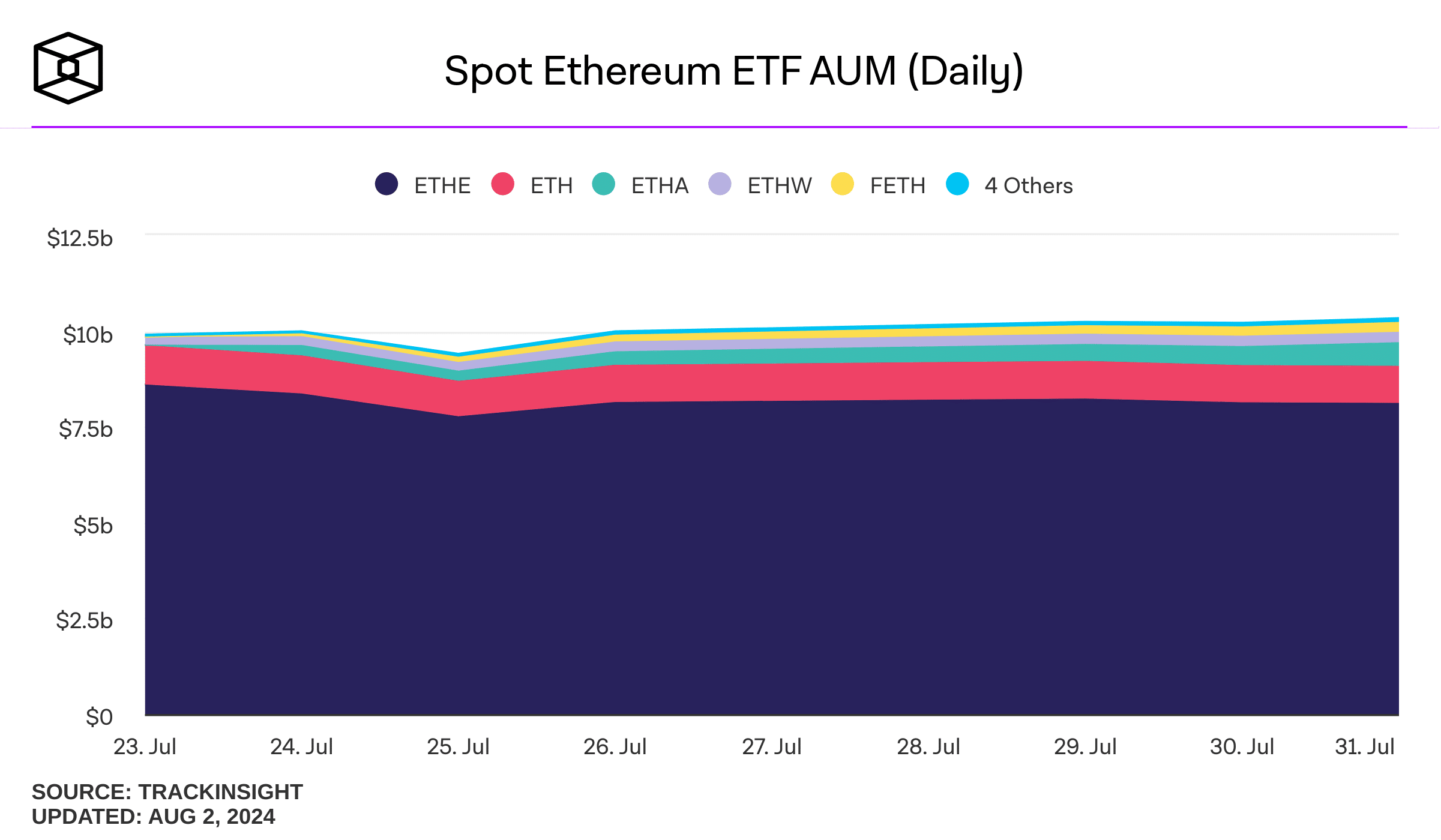
In the first week after the SEC approval, the nine funds hold about $10 billion worth of Ethereum, with Grayscale accounting for the lion’s share.
Source: The Block
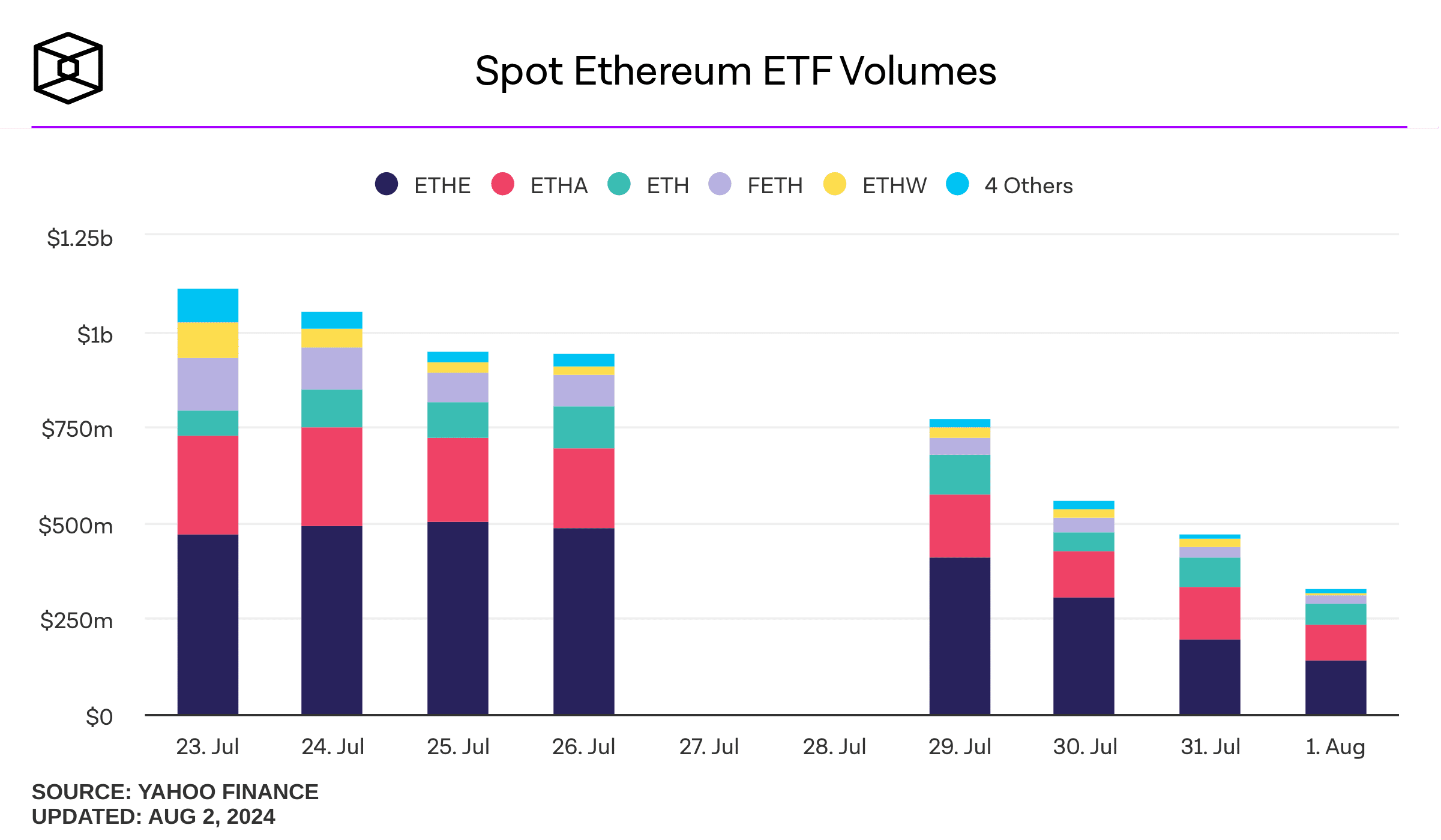
Ethereum ETF volumes declined during the first eight days of trading, but the same was true for Bitcoin ETFs as well.
Source: The Block
Ethereum ETF Pros
- Direct exposure to Ethereum in a regulated market.
- With Ethereum ETFs, investors can diversify traditional portfolios.
- Trading Ethereum ETFs doesn’t require investors to deal with digital wallets and complex crypto operations.
Liquid investment products backed by physical Ethereum held in a secure vault.
Ethereum ETF Cons
- Investors don’t own Ethereum directly.
- Investors can buy or sell the ETFs during market hours on business days only.
- Ethereum ETFs incur management fees and operational costs.
- Ethereum ETFs are less accessible for non-US residents.
- Ethereum ETFs don’t provide the same privacy as physical Ethereum.
Unlike physical Ethereum, the ETFs cannot be used for staking.
Ethereum vs. Ethereum ETFs: 5 Key Differences
Here are the main differences between Ethereum and its related ETF products:
#1 Ownership
The main difference between Ethereum and the related ETF products lies in the type of asset one holds. Ethereum is a cryptocurrency hosted on a decentralized network consisting of computers dispersed all over the world (nodes). The cryptocurrency is held in digital wallets and can be transferred to other crypto addresses or traded via centralized and decentralized exchanges.
Ethereum holders can also stake it – a form of passive income – through one of multiple types of staking platforms, including liquid staking protocols or restaking protocols.
With ETFs, investors own shares of the funds backed by Ethereum. The share price mirrors the performance of the underlying cryptocurrency. ETF investors cannot transfer their shares to digital wallets, redeem their shares for crypto, or stake them. Instead, the ETFs can be sold or redeemed for cash.
#2 Regulatory Oversight
The Ethereum blockchain represents a decentralized network that has no governing authority, with consensus being achieved collectively. After years of confusion, the SEC is treating Ethereum as a commodity, meaning that it falls under the supervision of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
Ethereum ETFs are securities and thus regulated by the SEC. They are issued by companies and registered with the securities watchdog.
#3 Liquidity and Accessibility
Ethereum can be traded on crypto exchanges like Coinbase or purchased with other crypto assets through wallets like tastycrypto. Buying ETH directly and storing it safely can be more complicated for non-tech-savvy traditional investors.
Elsewhere, Ethereum ETFs are more liquid, being available on traditional stock exchanges like Nasdaq, NYSE Arca, or Cboe’s BZX Exchange. ETF shares can be traded through brokerage accounts like tastytrade, Fidelity, or Robinhood, making them a great choice for traditional investors.
Also, while you can trade Ethereum at any time, ETH ETFs are available during trading days between 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM ET.
#4 Management Structure & Fees
ETH holders are responsible for managing their investments, which includes purchasing crypto through a reputable exchange and storing it in a secure wallet.
In contrast, with Ethereum ETFs, the issuing company handles all the behind-the-scenes work, including storing the digital asset safely in a cold wallet. This comfort comes at a price, as ETF issuers charge a management fee that can range from 0.15% to as high as 2.5%. Grayscale’s ETHE fund, for example, has a fee of 2.5%, which led to outflows of $2 billion in the first days due to the high management cost.
#5 Taxes
In the US, operations with both Ethereum and Ethereum ETFs can be taxable events. Investors must track their capital gains and losses in USD terms on their own, with each Ethereum or ETF transaction being treated as a taxable event.
When holding Ethereum ETF shares for less than a year before selling, the capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, ranging from 10% to 37%. Holding the ETF shares for more than a year before selling results in long-term capital gains, which are taxed at lower rates of 0%, 15%, or 20%.
FAQs
What are Ethereum ETFs?
Ethereum spot exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment funds registered with the US SEC that provide direct exposure to Ethereum by holding physical Ether coins and are traded on US stock markets.
What are the pros and cons of Ethereum ETFs?
Ethereum ETFs provide direct exposure to Ethereum in a regulated market, allow portfolio diversification, eliminate the need for digital wallets and complex crypto operations, and offer a liquid investment product.
How do Ethereum ETFs differ from Ethereum?
Ethereum is a cryptocurrency held in digital wallets and traded on crypto exchanges, while Ethereum ETFs are shares of funds backed by Ethereum, traded on traditional stock exchanges. In the US, Ethereum is treated as a commodity while the ETFs are securities.
Do Ethereum spot ETFs pay dividends?
No, Ethereum spot ETFs do not pay dividends, as current SEC regulations have removed provisions for staking from ETF filings before approval.
🍒 tasty reads



Solana’s Competition: Meet SUI and APT

Why Timing Matters: Crypto Market Signals to Watch

Upgrade Your Crypto Game: tastycrypto’s Biggest Update Yet