Definition: Arbitrage is the practice of profiting from price discrepancies by buying and selling assets in different markets. Just as in TradFi, there are arbitrage opportunities in DeFi.
Written by: Andrey Sergeenkov | Updated June 24, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace
In this article, we will explore some of the most popular arbitrage strategies used in crypto.
🍒 tasty takeaways
DeFi arbitrage capitalizes on price or interest rate disparities across decentralized platforms, presenting profit opportunities.
Triangular arbitrage exploits price variances among three assets within a single platform, enabling profitable trades between these assets.
Cross-exchange arbitrage seizes price discrepancies for identical assets across distinct platforms, purchasing cryptocurrency at a low price on one exchange and selling at a higher price on another platform.
Yield arbitrage benefits from interest rate gaps between platforms, lending at elevated rates on one platform while borrowing at lower rates on another.
Trade batching and flash loans arbitrage combine multiple trades in one transaction, using flash loans to execute complex strategies without upfront capital, and profiting from the difference in asset prices.
DeFi Arbitrage Summary
| Strategy | Definition |
|---|---|
| Triangular Arbitrage | Exploits price differences among three assets within a single platform. |
| Cross-Exchange Arbitrage | Capitalizes on price discrepancies for identical assets across different platforms. |
| Yield Arbitrage | Benefits from interest rate disparities between platforms. |
| Market Making | Provides liquidity to earn yields from trades, with potential risks like impermanent loss. |
| Trade Batching and Flash Loans Arbitrage | Combines multiple trades in one transaction, utilizing flash loans for executing strategies without initial capital. |
Intro to DeFi Arbitrage
DeFi, or decentralized finance, is a movement that aims to create a new transparent, permissionless, and programmable financial infrastructure using blockchain technology. DeFi platforms offer various services such as on-chain lending & borrowing, crypto trading, staking, and more.
However, DeFi platforms are also decentralized and operate on different blockchains, smart contracts, and liquidity pools. This means that they may not always represent the same prices or interest rates for the same digital assets. This creates opportunities for arbitrage, which is the practice of taking advantage of price or interest rate differences across different platforms or protocols.
In this article, we will explore what DeFi arbitrage is and how it works. You will learn some of the most common and popular DeFi arbitrage strategies and how to execute them.
🍒 In DeFi “MEV bots” are used to initiate many arbitrage opportunities. Learn how MEV bots work here!
What is DeFi Arbitrage Trading and How Does It Work?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are platforms that allow users to trade crypto assets without intermediaries. They also offer opportunities for arbitrage, a strategy that exploits price or interest rate differences across DEXs.
Arbitrage can be lucrative due to inefficiencies and volatility in the crypto market. Crypto assets arbitrage can be done manually or automatically with smart contracts, flash loans, or trading bots.
DeFi Arbitrage Risks
Some DeFi arbitrage risks to keep in mind include:
Smart contract bugs
Asset price fluctuations
Frontrunning attacks
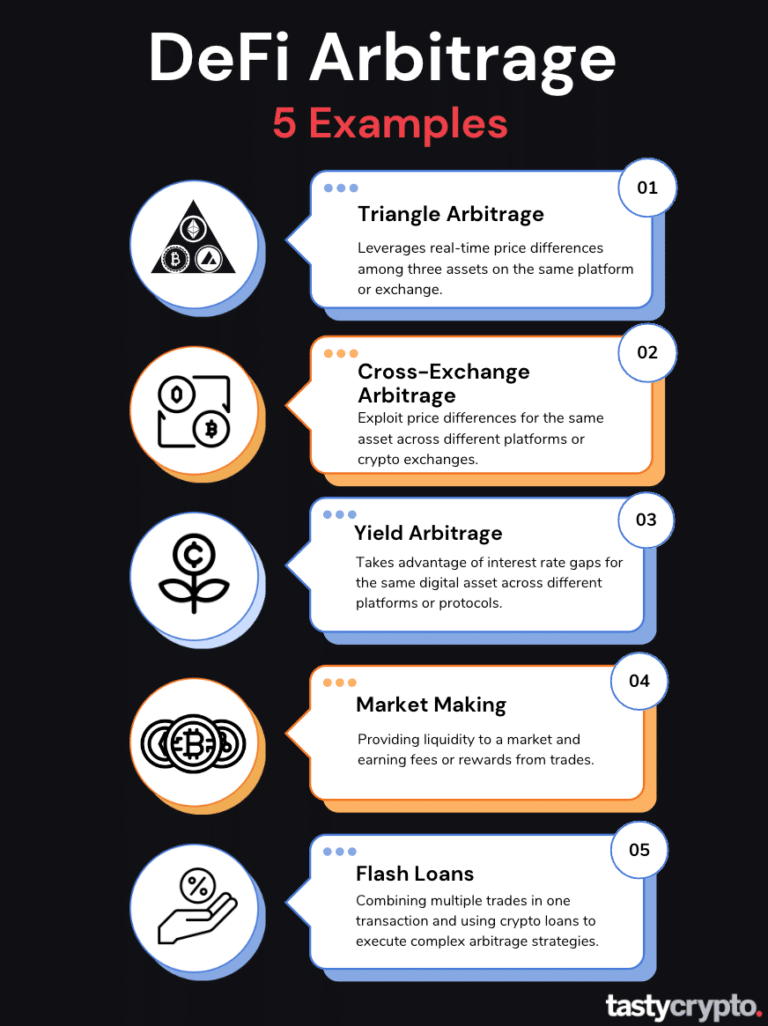
5 Arbitrage Trading Strategies to Know
DeFi arbitrage is not a one-size-fits-all strategy. There are various ways to execute it, depending on the platform and the market conditions. Some of these ways involve decentralized applications (dApps), while others include centralized exchanges (CEXs) like Binance, Okex, etc.
In this section, we will cover some of the most popular and effective DeFi arbitrage strategies and how they work.
1. Triangular Arbitrage
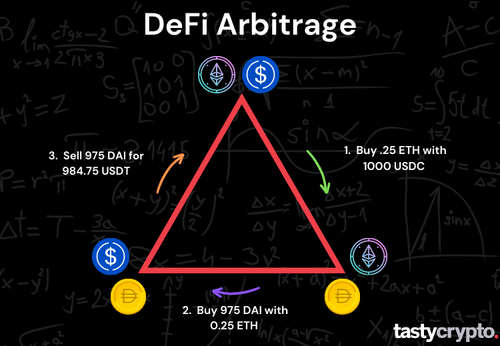
This is a strategy that leverages real-time price differences among three assets on the same platform or exchange. For example, if you can buy ETH with USDT, then buy DAI with ETH, then sell DAI for USDT, and end up with more USDT than you started with, you have performed a triangular arbitrage.
Suppose you have 1000 USDC and you see the following prices on Uniswap:
1 ETH = 4000 USDC
1 DAI = 1.01 USDC
1 ETH = 3900 DAI
You can perform a triangular arbitrage by:
Buying 0.25 ETH with 1000 USDC
Buying 975 DAI with 0.25 ETH
Selling 975 DAI for 984.75 USDT
You will have made a profit of 15.25 USDC minus transaction fees.
2. Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
This involves exploiting price differences for the same asset across different platforms or crypto exchanges. For example, if you can buy ETH for a lower price on Uniswap and sell it for a higher price on Kyber, you have performed a cross-exchange arbitrage.
Suppose you have 1 ETH and you see the following prices on Uniswap and Kyber:
1 ETH = 4000 USDT on Uniswap
1 ETH = 4100 USDT on Kyber.
You can perform a cross-exchange arbitrage by:
Buying 1 ETH for 4000 USDT on Uniswap
- Selling that 1 ETH for 4100 USDT on Kyber:
You have made a profit of 100 USDT minus gas price.
3. Yield Arbitrage
This is a strategy that takes advantage of interest rate gaps for the same digital asset across different platforms or protocols.
For example, if you can lend DAI at a higher rate on Compound and borrow DAI at a lower rate on Aave, you have performed a yield arbitrage.
Suppose you have 1000 DAI and you see the following interest rates on Compound and Aave:
Compound offers 10% APY for lending DAI and 12% APY for borrowing DAI
Aave offers 8% APY for lending DAI and 10% APY for borrowing DAI
You can perform a yield arbitrage by lending 1000 DAI on Compound and earning 100 DAI in a year, then borrowing 1000 DAI on Aave and paying 100 DAI in a year. You have made a profit of zero minus gas fees, but you have also gained access to another 1000 DAI that you can use for other purposes.
4. Market Making
Though not directly arbitrage, market making is a popular way to earn yield in DeFi.
This process involves providing liquidity to a market and earning fees or rewards from trades. For example, you can deposit ETH and DAI into a Uniswap pool and earn fees from every swap that involves ETH or DAI.
Suppose you have:
1000 USDT and 0.25 ETH
And you see the following prices on Uniswap:
1 ETH = 4000 USDT
You can perform market-making by depositing your USDT and ETH into the Uniswap pool and earning fees from every trade that involves USDT or ETH. For example, if someone swaps 100 USDT for 0.025 ETH, you will earn a fee of 0.3% of the trade value, which is 0.3 USDT or 0.000075 ETH.
A risk associated with crypto market making is impermanent loss.
📚 Read: What Are Automated Market Makers (AMMs)?
5. Trade Batching and Flash Loans Arbitrage
This involves combining multiple trades in one transaction and using flash loans to execute complex arbitrage strategies and algorithms without upfront capital.
An example of a trade batching and flash loan would be if you:
Borrow DAI from Aave using a flash loan
Swap it for ETH on Uniswap
Swap it for USDT on Kyber
Repay the flash loan to Aave
Keep the difference in USDT stablecoin
Suppose you have no capital or crypto assets and you see the following prices and interest rates on Aave, Uniswap and Kyber:
Aave offers flash loans for DAI at a fee of 0.09%
Uniswap offers 1 DAI = 1.01 USDT
Kyber offers 1 DAI = 1.02 USDT
You can perform a batching and flash loans arbitrage by:
Borrowing 10000 DAI from Aave using a flash loan
Swapping it for 10100 USDT on Uniswap
Swapping it for 9901.96 DAI on Kyber
Repaying the flash loan to Aave with a fee of 9 DAI
Keeping the difference of 7.04 DAI minus gas fees
Conclusion
DeFi arbitrage is a profitable but tricky way to make passive income in the DeFi space. It involves exploiting price or interest rate gaps across different exchanges and different markets using various strategies and tools. But DeFi arbitrage also demands technical skills, market knowledge, and risk management.
DeFi arbitrage opportunities are always changing and evolving as new platforms and protocols pop up. So DeFi arbitrageurs need to keep up and adapt to the dynamic DeFi landscape.
DeFi Arbitrage FAQs
The best time to find DeFi arbitrage opportunities is during volatile markets when prices are out of alignment. Some tools to find DeFi arbitrage include price trackers, bots, and market depth analyzers.
Some DeFi arbitrage strategies include price discrepancy (stablecoins included), interest rate discrepancy, flash loans, and exploiting imbalances in liquidity pools.
The most straightforward DeFi arbitrage opportunity involves taking advantage of price differences. When a token is trading at a lower price on one DEX compared to another, you can purchase it at the lower price and then sell it immediately for a profit on the DEX where it is trading higher. It’s important to consider any DEX fees and gas fees that may be incurred when executing these trades.
No, crypto arbitrage is not illegal. In all markets (not just crypto) arbitrage helps to increase market liquidity.
Arbitrage involves making profits by taking advantage of price differences, while hedging is a strategy used to safeguard existing position(s) from potential losses.
Making a living through crypto arbitrage can be extremely difficult unless you own a substantial amount of capital or have expertise in the field of cryptocurrencies.

Andrey Sergeenkov
Expertise: DAOs, NFTs. Blockchain. Cryptocurrency
Summary: 6 years of experience in the blockchain and cryptocurrency industry. Content Manager at DAO Time. Published in Cointelegraph, Coindesk, and Coinmarketcap.
🍒 tasty reads

What Is Ether.fi? Liquid Staking Reinvented

What Is Wrapped Ether? Complete wETH Guide

Impermanent Loss in DeFi: The Complete Guide

What is GMX? DeFi Perpetual Exchange 2024 Guide

What Is Defi Liquidity Mining and How Does It Work?


