ADA is the native token of the Cardano network while SOL is the native token of the Solana network. Both are proof-of-stake coins, but Solana offers lower fees and faster speeds. Additionally, the Solana network has much higher adaptability than Cardano.
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated August 9, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows

Cardano is a decentralized blockchain network that places a strong emphasis on academic research. Solana is a decentralized blockchain that offers incredibly high transaction throughput. Solana has a higher market cap and a higher total-value locked (TVL) in DeFi.
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
- ADA is Cardano’s native coin; SOL is Solana’s.
- Both use proof-of-stake but Solana also uses proof-of-history for speed, while Cardano is research-focused.
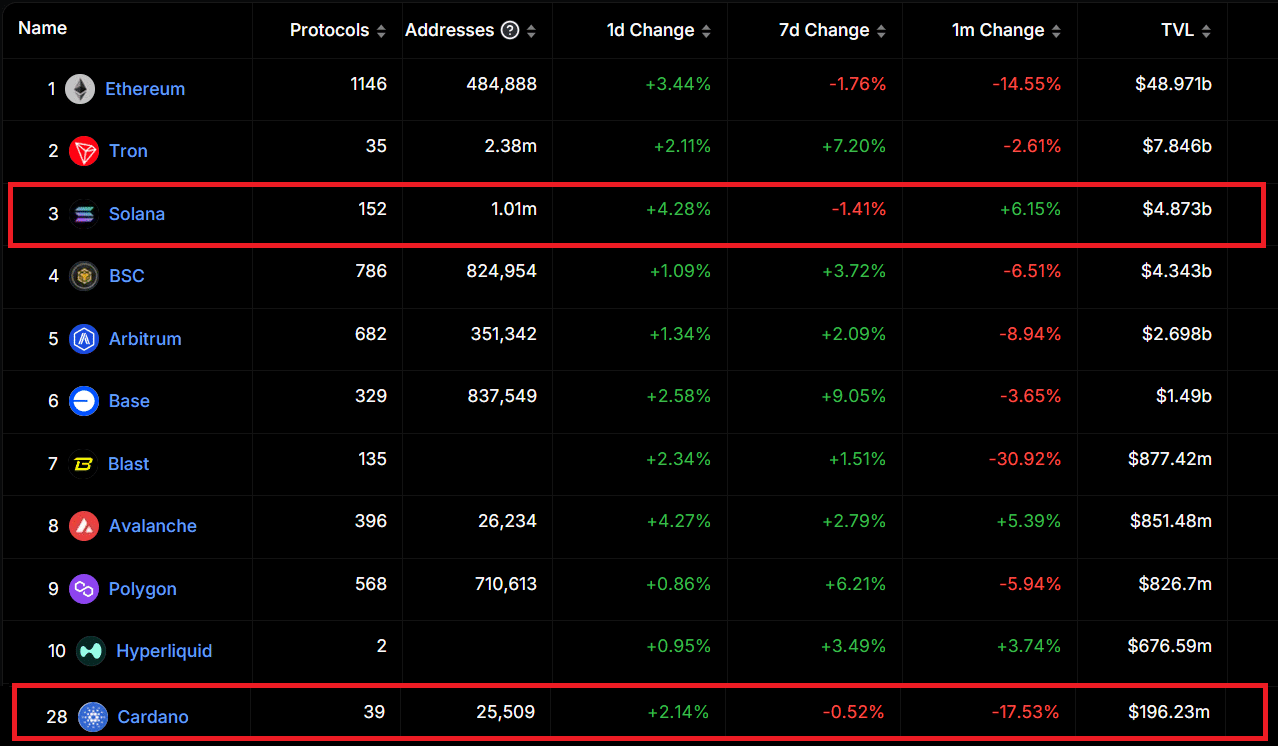
- In August of 2024, Cardano’s market cap is $12B, Solana’s is $67.2B. Solana’s TVL is $4.8B, Cardano’s is $196M.
- Solana’s programming language is Rust; Cardano uses Plutus.
- Both have lower fees than Ethereum and are scalable.
- Both support smart contracts and Web3 adoption.
Cardano (ADA) vs Solana (SOL): Overview
Both Cardano and Solana are peer-to-peer proof-of-stake blockchains that operate in a similar manner to the Ethereum blockchain. Let’s look at a table describing these platforms and then dive into the article!
| Criteria | Cardano (ADA) | Solana (SOL) |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy and Goals | Scientific approach, sustainability, security, and interoperability | Efficiency, high transaction throughput, low fees |
| Consensus Mechanisms | Ouroboros PoS protocol | Proof-of-history (PoH) and proof-of-stake |
| Market Capitalization (August 2023) | $21.6 billion | $45 billion |
| Total-Value Locked (TVL) | $454 million | $3.4 billion |
| Programming Language | Plutus (native smart contract language) | Rust |
| Transaction Fees | ~$0.25 | ~$0.00015 |
| Other Similarities | Both are scalable, use proof-of-stake, support smart contracts, Web3 adoption, have similar market caps, can be staked, and more. | |
ADA vs SOL: What’s the Difference?
Here are the main differences between the Cardano (ADA) and Solana (SOL) blockchains.
1. ADA vs SOL: Philosophy and Goals
Cardano takes a scientific approach to blockchain technology. This research extensive chain is laser-focused on sustainability, security, and interoperability.
Solana’s ambitions revolve more around efficiency. High transaction throughput and low fees are just a few reasons why developers prefer to build decentralized applications (dApps) on Solana over Cardano.
2. ADA vs SOL: Consensus Mechanisms:
Both blockchains rely on the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism but Solana also incorporates a proof-of-history (PoH) mechanism while Cardano solely relies on the Ouroboros PoS protocol.
One significant benefit of PoH is that this mechanism improves significantly Solana’s ability to scale. This is because PoH can easily verify previous transactions while at the same time minimizing the amount of data storage required.
💡 Proof-of-stake networks like Solana and Cardano can be 99% more energy efficient than proof-of-work networks like Bitcoin!
3. ADA vs SOL: Market Capitalization
In August 2024, Cardano had a market capitalization of $12 billion. At the same time, Solana had a market cap of $67 billion. Generally speaking, a larger market cap often correlates with reduced volatility.
4. ADA vs SOL: Total-Value Locked (TVL)
The total-value locked (TVL) of Solana is currently $4.8 billion. The TVL of Cardano is $200 million. Solana’s TVL, therefore, is about 25x the size of Cardano’s. Higher TVLs coincide with higher adoption.
5. ADA vs SOL: Price Action
ADA vs SOL: Fees
Solana charges very low transaction fees (~$0.00015) while Cardano charges a relatively higher fee (~$0.25). Both of these network fees, however, are dramatically lower than Ethereum and Bitcoin.
🍒 Solana (SOL) Price Prediction: 2025, 2030, 2040 & 2050
ADA vs SOL: Programming Language
The core programming language of Solana is Rust. Plutus is the native smart contract language for the Cardano blockchain.
ADA & SOL: What Do They Have In Common?
- Both Cardano and Solana charge significantly lower gas fees than the Ethereum mainnet.
- Both blockchains are decentralzied.
- Both blockchains are scalable.
- Cardano and Solana both use proof-of-stake.
- Both chains are integrated with the Web3 ecosystem.
- Cardano’s ADA and Solana’s SOL have similar market caps.
- Both ADA and SOL can be staked to earn passive income.
- ADA and SOL are both altcoins.
- Both networks are accessed through decentralized self-custody wallets.
- Both networks rely upon validators to add new blocks.
🍒 You can move crypto between blockchains like Cardano and Solana with ‘bridges’. Learn how bridges work here! 🍒
ADA vs SOL: How Do These Blockchains Work?
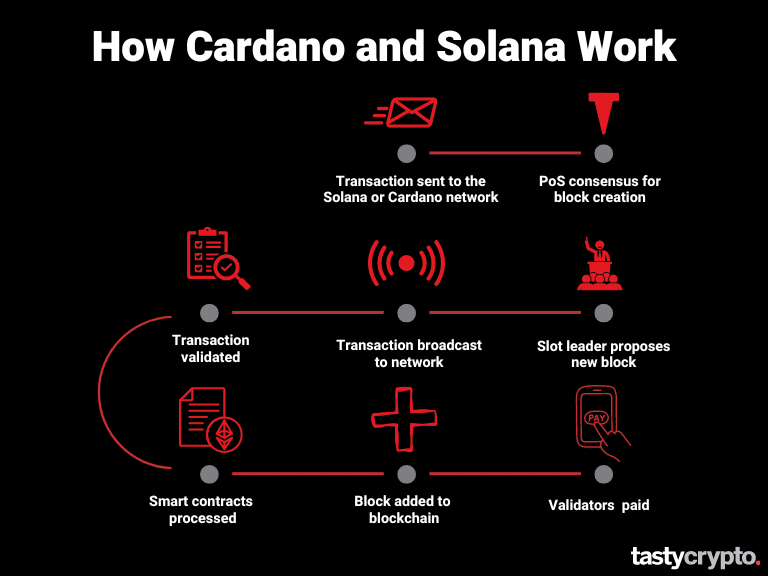
The below visual shows an overview of what happens behind the scenes when a transaction is sent to either Cardano or Solana.
What Is Cardano and How Does It Work?
Launched in 2017 by Charles Hoskinson, the Cardano network has grown to be the fifth most popular blockchain in terms of market cap. Cardano differentiates itself from other blockchains in its research-driven approach. Here’s what the Cardano whitepaper says:
"Rooted in rigorous academic and scientific research, Cardano distinguishes itself by emphasizing a research-driven approach, ensuring each protocol and feature undergoes meticulous peer-review processes before being implemented."
— Cardano Whitepaper
Unlike most blockchains, Cardano is structured in two distinct layers: the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) and the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL). The former focuses on cryptocurrency transactions while the latter allows for the execution of smart contracts. Dividing Cardano into two layers has made the network more agile and adaptable.
What Is Solana and How Does It Work?
Launched in 2020 by Anatoly Yakovenko, Solana is a leader in the world of decentralized applications. Solana attracts developers because this blockchain offers high transaction throughput and low network fees. Let’s go to the Solana whitepaper!
"The Leader sequences user messages and orders them such that they can be efficiently processed by other nodes in the system, maximizing throughput."
— Solana Whitepaper
The price of Solana fell dramatically on the tail of the FTX collapse. This is because Sam Bankman-Fried (the founder of FTX) had a significant stake in the Solana network’s ecosystem. However, in early 2024, the price of Solana has rebounded considerably and is up over 300% in the last year.
Source: DeFillama.com
Solana vs Cardano FAQs
Both Solana (SOL) and Bitcoin (BTC) function as distinct blockchains. However, Solana has the ability to execute smart contracts, whereas Bitcoin’s network primarily handles basic transactions.
Solana is the better investment for those who believe in the future of Web3 as this blockchain has 3x the amount of total value locked when compared to Cardano. Cardano, on the other hand, has a higher market cap than Solana and therefore experiences slightly less volatility.
Some benefits of Solana include high transaction throughput, low transaction fees, smart contract compatibility, short transaction times, and a rapidly growing ecosystem.
The main difference between Solana and Cardano is that Solana incorporates proof-of-history and proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms while Cardano relies only on a proof-of-stake mechanism. Additionally, Cardano is generally a slower network than Solana.
Solana’s SOL may prove to be a good investment for those who believe that Web3 adoption will both grow and scale.
Solana serves as an alternative to the Ethereum blockchain. Though it may not match Ethereum’s extensive adoption, Solana provides more affordable transaction costs and boasts quicker processing times. Additionally, Solana is quicker to fix scalability concerns.
Yes, Solana supports smart contracts that validate ownership of digital assets such as non-fungible tokens (NFTS).
Though most crypto market participants favor Cardano (ADA) because of its superior market cap, Solana (SOL) has greater real-world use cases as this blockchain supports more on-chain activity and has a much greater presence in decentralzied finance (DeFi).

Mike Martin
Mike Martin formerly served as the Head of Content for tastycrypto. Before joining tastycrypto, Michael worked in the active trader divisions of thinkorswim, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. He also served as a writer and editor for projectfinance.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences