Investing in Bitcoin ETFs provides price exposure without actual BTC ownership, diverging from Bitcoin’s principle of financial sovereignty. Conversely, blockchain and Bitcoin ETFs broaden access for those seeking involvement in digital assets and blockchain technology without the direct management complexities.
Written by: Anatol Antonovici | Updated March 6, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace

Bitcoin ETFs have been making waves since their launch at the beginning of 2024. So how do they differ from actual Bitcoin? Let’s find out! 🏃
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
Bitcoin ETFs are investment funds offering indirect exposure to Bitcoin.
Bitcoin ETFs track the price of Bitcoin but offer a distinct experience: they are listed on regulated stock exchanges and are accessible exclusively during market hours.
Bitcoin ETFs were approved in mid-January 2024 and have attracted over $40 billion.
Summary
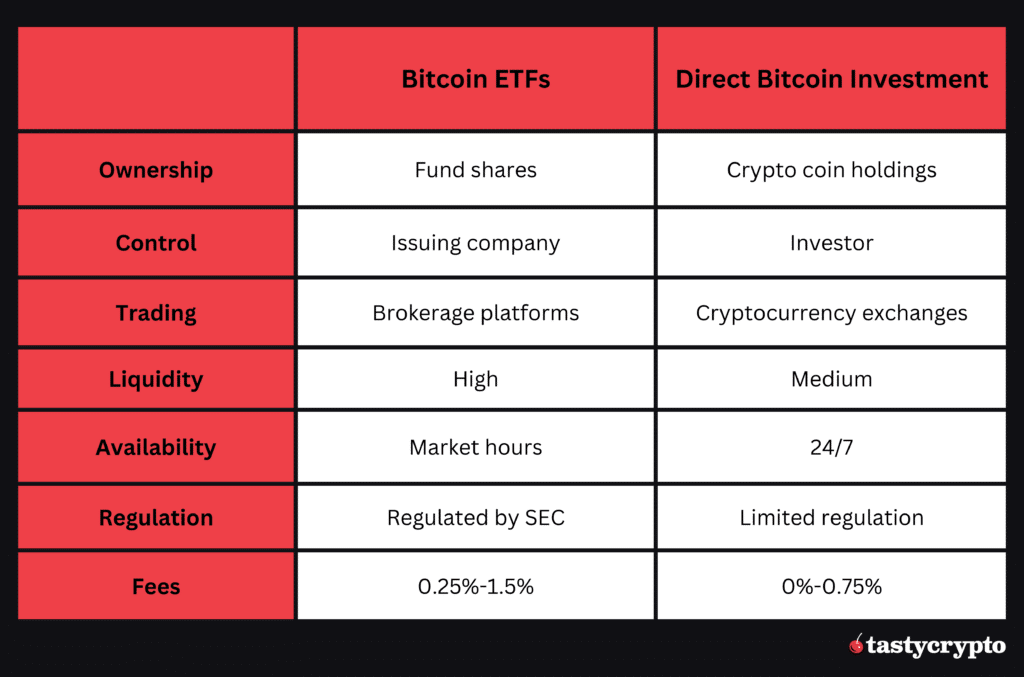
| Feature | Bitcoin | Bitcoin ETF |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Direct ownership with private key access. | Ownership of fund shares, not the actual Bitcoin. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Decentralized, lacks clear global regulation. | Regulated by entities like the SEC. |
| Liquidity & Accessibility | 24/7 trading on cryptocurrency exchanges. | Traded during stock market hours; broader investor access. |
| Market Hours | Available for trade anytime. | Accessible during market hours only. |
| Tax Implications | Each transaction could be a taxable event. | Potentially simplified tax reporting. |
| Management & Fees | Self-managed, potential network fees. | Managed by issuing company, includes management fees. |
What Are Bitcoin ETFs?
Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment funds giving investors direct exposure to Bitcoin.
The ETFs are investment products listed on traditional stock markets, being regulated by the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
After years of waiting, the SEC approved the first batch of BTC ETFs at the beginning of January 2024, accelerating the cryptocurrency’s recovery journey.
Spot Bitcoin ETFs are required to actually hold ‘physical’ crypto coins with a custodian, which enables investors to trade ETF shares securely through traditional brokerage platforms.
🍒 Crypto for Beginners: What Is Crypto and How Does It Work?
Current List of BTC ETFs and Their Performance
The SEC green-lit 11 ETFs in total. Some of the issuers include:
- Grayscale (GBTC)
- BlackRock (IBIT)
- Bitwise (BITB)
- VanEck (HODL)
- Fidelity (FBTC)
- Valkyrie (BRRR)
Bitcoin ETFs are a big deal, as they help cryptocurrency gain legitimacy on Wall Street, attracting capital from institutions and high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs).
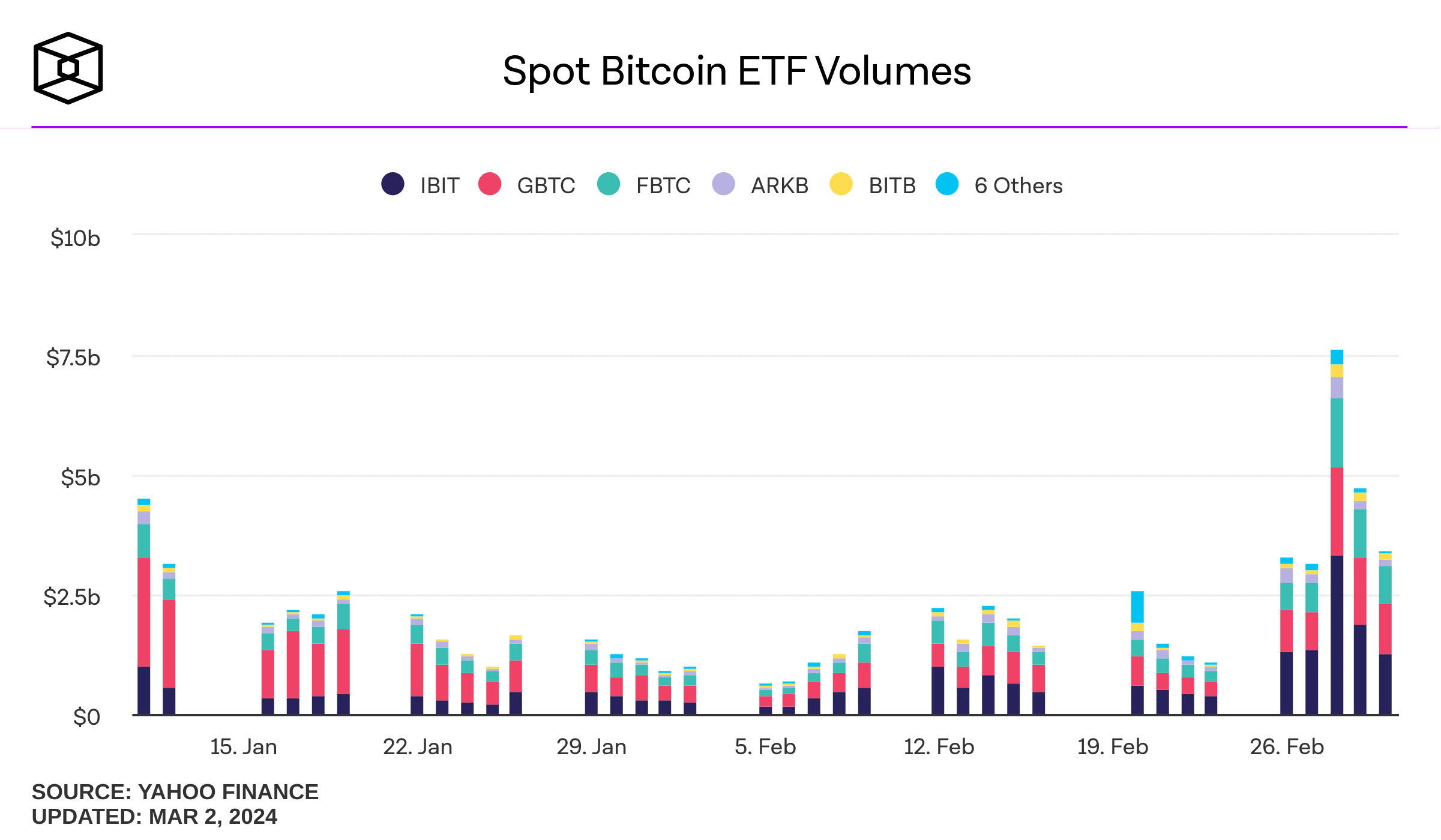
In the first two months following their launch, over $70 billion worth of ETF shares changed hands, with Grayscale Bitcoin Trust and BlackRock’s ETF accounting for the lion’s share.
Source: TheBlock
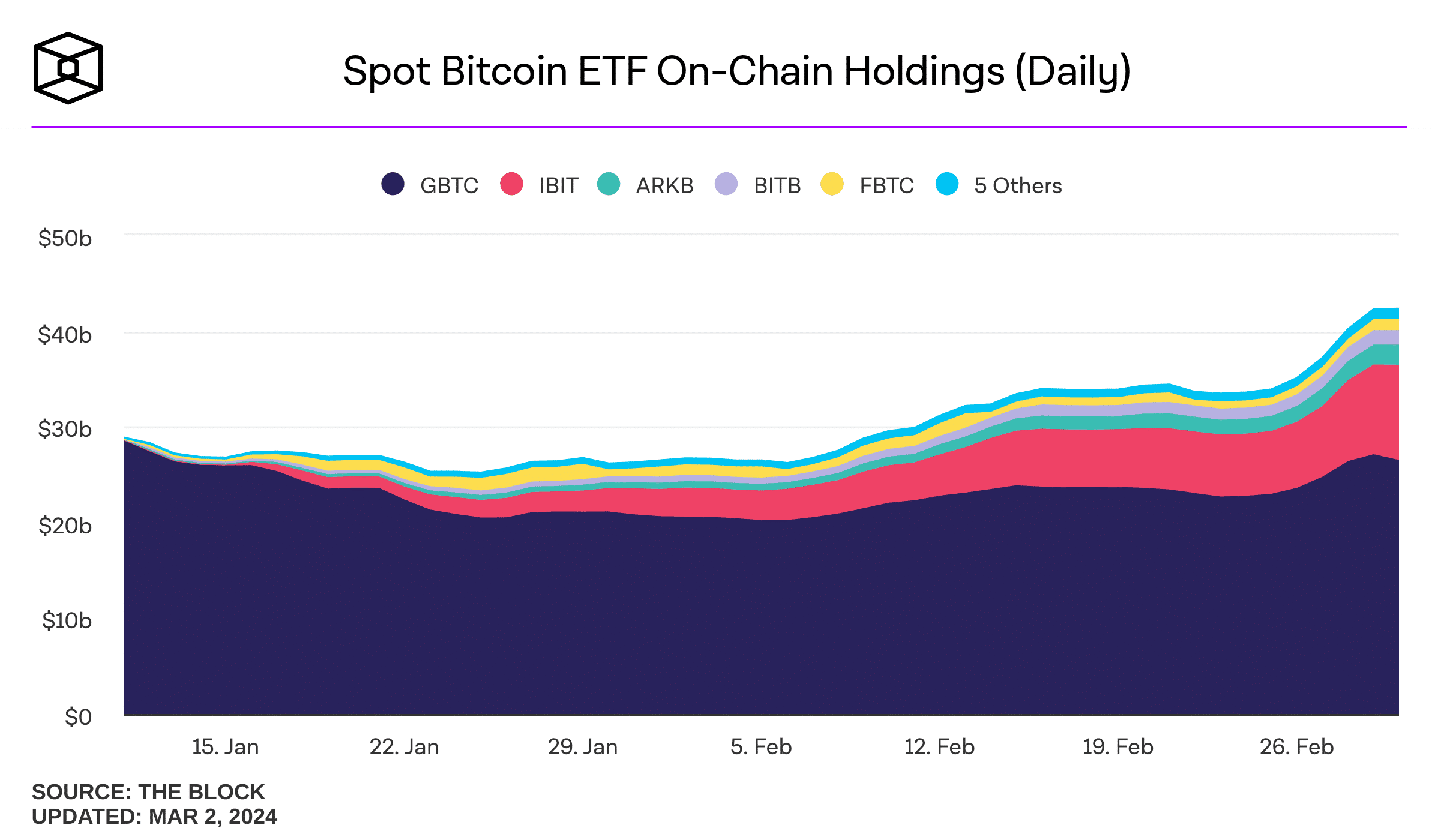
As of this writing, these funds hold over $40 billion worth of Bitcoin. 👇
Source: TheBlock
Bitcoin ETF Pros
- Direct exposure to Bitcoin in a regulated market.
- Liquid investment product, with physical Bitcoin being held in a vault.
- Ability to diversify traditional portfolios.
- Less complicated than trading actual BTC.
Bitcoin ETF Cons
- Investors don’t own the underlying Bitcoin.
- The ETFs are tradeable during market hours on business days only.
- ETFs have management fees and operational costs.
- Bitcoin ETFs are highly regulated and aren’t easily accessible to the world at large.
Bitcoin vs Bitcoin ETFs: 7 Differences
Below are the main differences between Bitcoin and its related ETF products:
#1 Ownership
With Bitcoin ETF, investors own shares of the funds, which can increase or decrease in value based on Bitcoin’s price performance. However, they cannot transfer crypto to digital wallets or redeem their shares for an equivalent amount of crypto.
Truly owning Bitcoin involves having direct access to your private keys, which Bitcoin ETF owners do not have. The only way to actually own Bitcoin is to hold it in a self-custody crypto wallet.
#2 Regulatory Oversight
While the prices of Bitcoin and its related ETFs may move in tandem, they are fundamentally different products.
A borderless, decentralized network with no governing authority runs Bitcoin.
In the United States, the regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies needs to be developed, lacking clear oversight. However, it is anticipated that digital assets will ultimately be subject to stringent regulation by a government agency.
Bitcoin ETFs, however, fall under the securities umbrella and are regulated by the SEC. They are issued by companies registered with the SEC.
In contrast, the decentralized nature of Bitcoin means there is no entity with the power to enforce regulatory compliance globally.
#3 Liquidity and Accessibility
Bitcoin is traded on specialized cryptocurrency exchanges, including platforms like Coinbase. Although cryptocurrency traders generally don’t face significant liquidity issues with BTC, Bitcoin ETFs offer even greater liquidity, appealing to conventional investors.
These ETF shares are listed on stock exchanges such as NASDAQ. They are accessible through brokerage accounts from providers like tastytrade, Fidelity, TD Ameritrade, and Robinhood, enhancing liquidity and accessibility for both retail and institutional investors.
In contrast, purchasing and securely storing Bitcoin directly involves a more complex process, which can be particularly challenging for traditional investors who are not technologically adept.
#4 Market Hours
While you can trade Bitcoin anytime, ETFs are available for trading during market hours (9:30 AM to 4:00 PM ET) on business days.
This can have serious consequences.
For example, if you buy ETF shares while Bitcoin (BTC) is trading at $60,000 on a Friday, you might see its value drop by 15% over the weekend, during which time you’re unable to sell your shares. In contrast, actual Bitcoin can be traded 24/7, allowing for more flexibility in responding to market fluctuations.
#5 Tax Implications
As a rule, each transaction involving Bitcoin or a Bitcoin ETF is treated as a taxable event, and investors are responsible for tracking their capital gains and losses in dollar terms over the course of a year.
In this scenario, ETF investors have an advantage because ETF issuers typically provide regular reports, which can simplify the process of filing taxes.
The IRS assesses Bitcoin ETF-related capital gains based on the holding period, e.g., short-term gains are taxed differently from long-term gains.
When you sell Bitcoin ETF shares held for less than a year, the capital gains are taxed at ordinary income rates, which vary from 10% to 37%. Conversely, if you hold the shares for over a year before selling, the long-term capital gains are subject to lower tax rates, specifically 0%, 15%, or 20%.
#6 Management Structure & Fees
Bitcoin holders are tasked with directly managing their investments, which involves ensuring the security of their crypto wallets and selecting a reputable exchange for transactions.
In contrast, when investing in Bitcoin ETFs, the issuing company manages the operational aspects, such as securely storing the cryptocurrency in vaults and monitoring its market price.
However, trading Bitcoin ETF shares usually involves higher costs. Most Bitcoin ETFs, offered by companies like BlackRock, Fidelity, and VanEck, charge a trading fee of 0.25%. Grayscale’s GBTC, representing over 60% of all Bitcoin ETF holdings, levies a 1.5% fee per trade.
It must be noted that transacting in bitcoin and other cryptos that you own outright often involves fees. For example, with self-custody wallets, you have to pay network fees, which can fluctuate wildly. With exchange wallets, you pay maker/taker fees.
#7 Ecosystems
Bitcoin ETFs can be easily integrated into traditional portfolios, as they’re no different than company shares. However, they cannot be directly converted to other crypto assets.
While Bitcoin outright ownership cannot be directly integrated into traditional portfolios, you can easily trade it against other digital assets on crypto exchanges and even participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) opportunities through Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC).
Secure Your Crypto With Self-Custody
When you store your crypto in a self-custody wallet, you don’t have to trust that an exchange is acting in your best interest. This is because you are the only party privy to your private key, or seed phrase.
Here are some additional benefits you get when you choose to self-custody your digital assets with tastycrypto:
- In-App Swap: Trade BTC, ETH, and 1,000+ tokens
- Generate Yield in DeFi: Stake, lend, and become your own market maker
- NFTs: Buy, sell, and view NFTs in-app
tastycrypto offers both iOS and Android self-custody wallets – download yours today! 👇
FAQs
A spot Bitcoin ETF is an investment vehicle that directly exposes you to Bitcoin. The fund holds actual crypto in a vault and issues ETF shares that can be traded on a stock exchange.
Bitcoin ETFs are tradable securities under the supervision of a regulator like the US Securities and Exchange Commission. Actual Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency on blockchain that can be stored in a digital wallet.
Spot Bitcoin ETFs have ‘physical’ Bitcoin reserves, while futures Bitcoin ETFs are derivatives that use complex approaches to mimic Bitcoin’s price movement without exposure. Therefore, spot ETFs are more secure and straightforward.
All Bitcoin ETFs are regulated, but it’s best to consider the funds with higher liquidity, such as BlackRock’s ishares Bitcoin Trust and Grayscale Bitcoin Trust.
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences


Anatol Antonovici
6+ years of experience writing for crypto brands and blockchain firms, including Coindesk, Cointelegraph, Bitcoinist, CryptoPotato, Algorand, and OTCTrade.com