Definition: Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer digital cryptocurrency that operates with no intermediaries.
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated June 25, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows
Bitcoin is the largest decentralized blockchain in existence. It’s native cryptocurrency is bitcoin (BTC). In this guide, we’ll teach you everything you need to know about the Bitcoin blockchain network and its native medium of exchange cryptocurrency bitcoin (BTC).
🍒 tasty takeaways
Bitcoin was the first successful blockchain network to launch.
Bitcoin operates without a central authority.
Satoshi Nakamoto wrote the Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008.
Bitcoin is currently the world’s largest crypto by market cap.
Bitcoin can be bought on either centralized or decentralized crypto exchanges.
Unlike Ethereum, bitcoin is not Turing-complete and therefore can not execute code (smart contracts).
Bitcoin (BTC) Summary
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin's Creation | Bitcoin, introduced in 2008, was the first successful blockchain network, offering a peer-to-peer digital currency system without intermediaries. |
| Bitcoin's Purpose | Initially designed to allow users to send currency online without banks, it's now mainly a secure store of value, similar to digital gold. |
| Bitcoin Security | Bitcoin offers security features like immutability, cryptographic protection, decentralization, miners' consensus mechanism, and a limited supply of 21 million coins. |
| How Bitcoins Are Made | Bitcoins are created by miners who add blocks to the blockchain. They earn bitcoins as rewards for this computational work. |
| Bitcoin vs Ethereum | While Bitcoin primarily serves as a store of value, Ethereum, introduced in 2015, offers smart contracts enabling decentralized applications (dApps), making it Turing complete. |
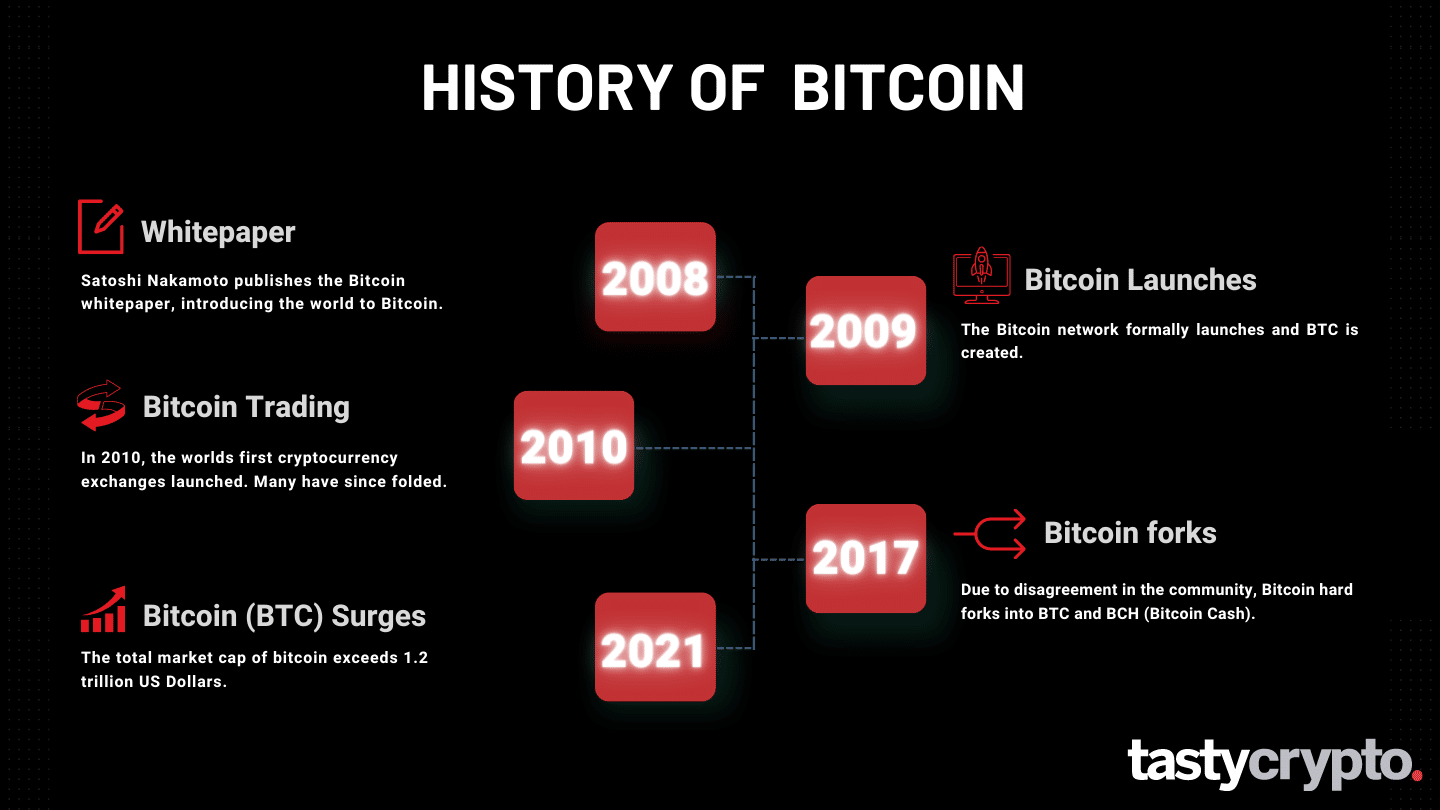
Bitcoin was the first successful blockchain network to come into existence. It is currently the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
The world was introduced to the idea of Bitcoin, and its native cryptocurrency bitcoin (BTC), in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto published their Whitepaper, “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”.
On Jan. 9, 2009, Bitcoin Block 1 was mined. It wouldn’t be until one year later that the first bitcoin was traded on an exchange. The asking price? $0.0008. Currently, bitcoin is trading at $61,300.
Bitcoin was built to act as an open-source digital payment system, but in 2024 most crypto participants use bitcoin as a store of value, like digital gold.
Bitcoin is unlike traditional currencies (fiat currencies) in that it operates devoid of a central bank.
🍒 Read! Bitcoin vs Bitcoin ETF
Why Was Bitcoin Successful?
Bitcoin was successful because it created a solution for a problem that plagued all previous attempts at blockchain technology: the double-spending problem.
Before Bitcoin, a trusted, centralized intermediary was required to assure that users did not spend more cryptocurrency than they had. The necessity of this third-party intermediary defeated the purpose of a peer-to-peer, decentralized network.
“In this paper, we propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server to generate computational proof of the chronological order of transactions.”
— Satoshi Nakamoto
What is The Purpose of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was initially created as a way for users to send currency over the internet without the need for a bank or regulatory approval.
Laszlo Hanyecz made the first documented purchase with bitcoin. He bought a pizza for 10,000 BTC. If Laszlo were to have saved that crypto instead of buying pizza with it, it would be worth over $613,000,000 US Dollars today!
In 2024, there are thousands of cryptocurrencies in existence. The more popular of these cryptos – ether (ETH), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL) – are much more efficient to transact with than bitcoin.
For this reason, bitcoin today is used primarily as a secure store of value, kind of like digital gold. Let’s next look at a few reasons why Bitcoin has become such a popular store of value.
📚 Read! Bitcoin Price Prediction: 2025, 2030, 2040 & 2050
Should You Buy Bitcoin?
At tastycrypto, we believe Bitcoin is a legit store of value and therefore a great portfolio diversifier. Watch this video to see why!
5 Reasons Why Bitcoin is Secure
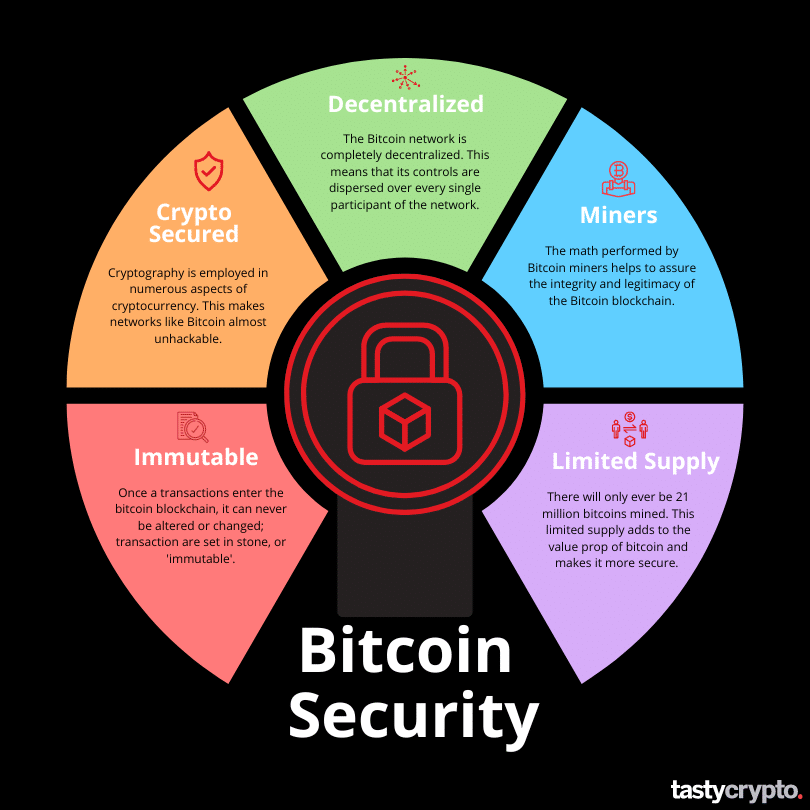
Here are the top five reasons that make bitcoin a secure investment.
1. Bitcoin is Immutable
Once a transaction goes into a Bitcoin block, that transaction can never be altered or changed. Something that can never be altered or changed is called ‘immutable’, which is another way of saying set in stone.
2. Bitcoin is Cryptographically Secure
Cryptography is employed in numerous aspects of cryptocurrency. In Bitcoin, cryptography is used to both generate private and public keys and for cryptographic hash functions.
Cryptography in Bitcoin has two purposes:
Securing the network from corruption.
Providing irrefutable ownership to parties holding digital assets.
3. Bitcoin is Decentralized
The Bitcoin network is completely decentralized. This means that its controls are dispersed over every single participant of the network. This diversification of control provides for an unparalleled system of checks and balances that centralized institutions can not match. This disbursement of control, in turn, increases security.
4. Bitcoin Uses Miners
There are thousands of different bitcoin miners in operation today. These miners add new blocks (and the transactions within them) to the blockchain by verifying transactions. This process involves miners checking for things such as ‘double-spending’. In order to ultimately add a block to the blockchain, the miner must perform intense mathematical computations using algorithms. This math helps to further secure the integrity of the Bitcoin blockchain. The greater the computing power you have the greater the odds you have of solving the math problem.
5. Limited Supply
It is difficult to assign value to an asset class that is infinite in supply. There will only ever be 21 million bitcoin mines. This limited supply adds to the value prop of bitcoin and makes it more secure.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
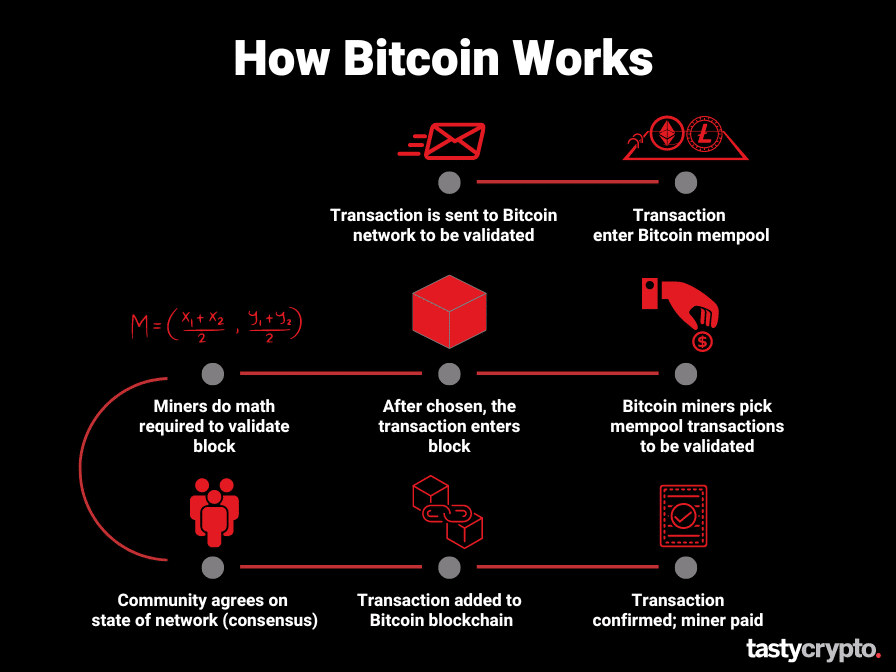
The below visual shows the journey every single bitcoin transaction must take in order to be confirmed.
Let’s now take a moment to learn how bitcoins are actually created.
How Are Bitcoins Made?
Every single bitcoin in existence (and every bitcoin to come) is created by the mathematical work performed by miners.
Bitcoin miners are responsible for adding new blocks (and all the transactions within them) to the immutable blockchain. The current block reward for their work on June of 2024 is 3.125 bitcoins, or about $191,500.
The competition to mine the latest block, as you can imagine, is intense. Because of the fierce competition, today it is 80+ trillion times more difficult to get the reward compared to day one.
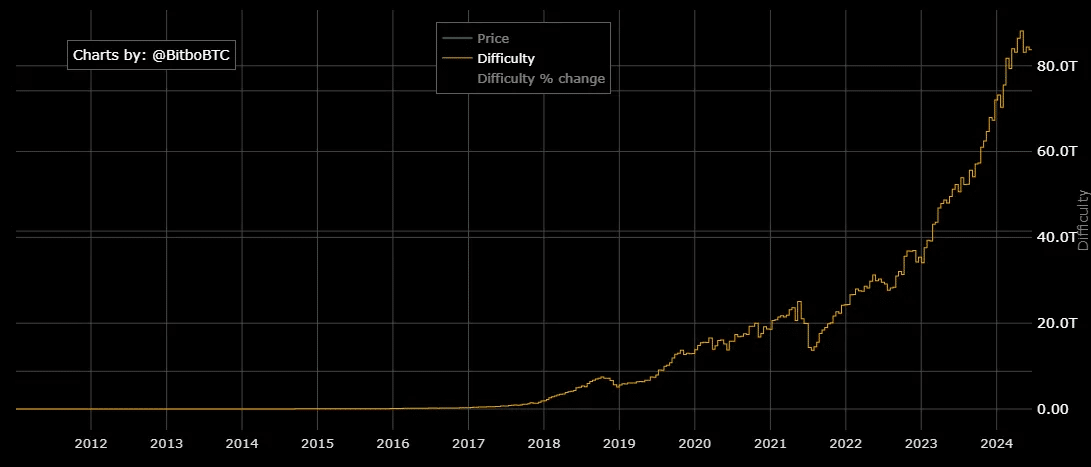
After miners get their reward, they can sell their bitcoin on an exchange, which ultimately trickles down to all crypto participants.
How Do You Buy Bitcoin?
There are two primary ways to buy and sell bitcoin: centralized crypto exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized crypto exchanges (DEXs). You don’t have to purchase an entire bitcoin – denomination in bitcoin go all the way down to one Satoshi (SATS), which is one hundred millionths of a bitcoin.
Read! CEX vs DEX – Crypto Exchange Fees Comparison
Centralized Crypto Exchanges
Buying cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin on centralized exchanges like Coinbase is much like buying stocks. You deposit cash in your account and make a trade to swap this cash for cryptocurrency.
The problem with buying bitcoin on a centralized exchange lies in the backend. On centralized exchanges (CEXs), your exchange maintains custody over your private keys. This means you can not trace your bitcoin on the blockchain to assure your exchange is holding your crypto 1X1.
FTX, for example, was actively trading their customer’s cryptocurrency. The lack of regulatory oversight allowed them to essentially steal their customer’s crypto for a very long duration of time.
Decentralized Crypto Exchanges
If you want complete control over your bitcoin (or any other digital assets you own), you will want to purchase crypto on a decentralized exchange.
In order to buy bitcoin on a decentralized exchange (DEX), you will need a digital wallet called a self-custody crypto wallet, such as the one tastycrypto offers.
Read: What is A Self-Custody Wallet and How Does it Work?
Your self-custody wallet is only connected to a DEX while you are making a trade.
After the trade is confirmed, you disconnect your wallet, thus eliminating any hacking risks (which are not uncommon in self-custody wallets).
Blockchain networks are not compatible with cash. Therefore, you must first purchase crypto on a centralized exchange, and then send it to your self-custody wallet to get started. Additionally, in order to buy bitcoin, you must first assure your wallet is a bitcoin wallet (the tastycrypto wallet is bitcoin compatible).
Top 5 Risks of Bitcoin
Volatility Risk
Perhaps the greatest risk associated with bitcoin is the cryptocurrency itself. Cryptocurrencies are a notoriously volatile asset class.
Regulation Risk
Decentralized blockchain networks like Bitcoin are currently operating with very little government intervention. This lack of regulatory oversight adds to the risks of investing in bitcoin (BTC). In theory, any government can ban cryptocurrencies at any time (as China did).
Transactions are ‘immutable’
All cryptocurrency transactions are immutable. That means that if you make a mistake (send crypto to the wrong party or make a trade in error) no central intermediary will be able to reverse the transaction.
Seed phrase risk
If you buy bitcoin with a self-custody crypto wallet, you alone are responsible for maintaining a record of your seed phrase. If this is lost, there is no way for you to recover your crypto. Of all bitcoin in existence, The New York Times estimates that 20% have been lost due to misplaced seed phrases
Scaling Risks
Unlike Ethereum, Bitcoin is a proof-of-work network (PoW). PoW networks are notoriously expensive and slow. These constraints may hinder Bitcoins growth, and diminish bitcoins value. Let’s read more on this next!
Bitcoin vs Ethereum
The Ethereum network launched in 2015. Ethereum, created by Vitalik Buterin, has one main advantage over Bitcoin: this blockchain can store basic transactions and code.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, can only store basic transactions.
On the Ethereum network, this code is deployed to the blockchain via smart contracts. Being able to store code makes Ethereum ‘Turing complete’.
For this reason, Ethereum has far greater utility than Bitcoin. In Web3, these smart contracts are the backend to decentralized applications (dApps). dApps are creating completely decentralized versions of the Web2 apps we use today.
🍒 Read! Blockchain bridges allow user to send crypto from Ethereum to Bitcoin
BTC vs ETH: Consensus Mechanisms
Another difference between Bitcoin and Ethereum lies in the consensus mechanisms they use.
Bitcoin uses the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism. In this model, bitcoin miners compete to validate blocks by solving complicated math problems. Bitcoin mining requires massive computational power.
Ethereum, on the other hand, has switched its consensus mechanism from PoW to proof-of-stake (PoS).
In PoS blockchains, the math required to secure the blockchain cryptographically is assigned to one computer, or ‘node’. In order to be eligible to do the math required to validate the latest block (and receive the rewards for doing so) you must stake ETH coins. The more ETH coins you stake, the greater the chance you have of being selected as a validator.
Anyone can stake ETH and earn the rewards that come with it.
BTC vs ETH: Fees
Lastly, the Ethereum network has lower transaction fees (gas fees) and higher throughput than Bitcoin.
At the end of the day, Bitcoin is seen mainly as a very secure store of value, kind of like digital gold. Ethereum is seen as a blockchain with high utility as it is being used to build thousands of different dApps.
🍒 Go In-Depth: What is Ethereum and How Does it Work?
Bitcoin Ordinals
Ordinal Inscriptions make it possible to imprint digital assets, such as images or text, onto a satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin (BTC). This enables the creation of distinctive NFT-like assets within the Bitcoin ecosystem, even though Bitcoin is typically considered fungible.
Comparatively, ordinals are akin to autographing a dollar bill – the bill remains fungible, but it gains a unique value
Bitcoin: Final Word
Bitcoin is the largest cryptocurrency in the world. For this reason, it is often the first coin new crypto investors purchase. Though bitcoin is one of the least volatile cryptocurrencies, it is still an incredibly volatile asset class. This article from sec.gov may be helpful in understanding the risks involved with investing in bitcoin.
📖 Read next! Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash vs Ethereum
FAQs
Yes, you can turn bitcoin (BTC) into cash (fiat currency). If you own your bitcoin on a centralized cryptocurrency exchange, this process is simple – just place a sell order. If you own bitcoin on a decentralized exchange, you will have to transfer that crypto to a centralized exchange in order to convert it to cash.
You can only purchase things with bitcoin (BTC) if the seller accepts bitcoin as a payment method. In 2024, more and more places are accepting cryptocurrency as a payment method.
When you purchase bitcoin, the seller of the bitcoin receives whatever you exchanged this bitcoin for. If you are buying bitcoin with a centralized exchange, they will either match your order with a bitcoin seller or clear the trade themselves. When you buy bitcoin on a decentralized exchange, you are swapping your bitcoin for another cryptocurrency via an automated market maker.
According to modern portfolio theory and the ‘market portfolio’, investing in a small amount of bitcoin is smart. Read: Here’s Why to Invest in Bitcoin
It is believed that Satoshi Nakamoto, the inventor of bitcoin, owns over 1 million bitcoins, making him the largest BTC owner in 2024.

Mike Martin
Mike Martin formerly served as the Head of Content for tastycrypto. Before joining tastycrypto, Michael worked in the active trader divisions of thinkorswim, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. He also served as a writer and editor for projectfinance.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads


Crypto Burning Guide: What It Means and How It Works

Crypto Coin vs Token: What’s The Difference?
Leverage in Crypto Trading: 6 Key Examples

What Is Slippage in Crypto? Beginners Guide