📕 Definition: Ethereum is a proof-of-stake cryptocurrency blockchain that is able to store and execute code.
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated June 14, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows

Ethereum is building the Web3 revolution. In this article, we’ll learn why Ethereum is second only to Bitcoin in the crypto world.
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
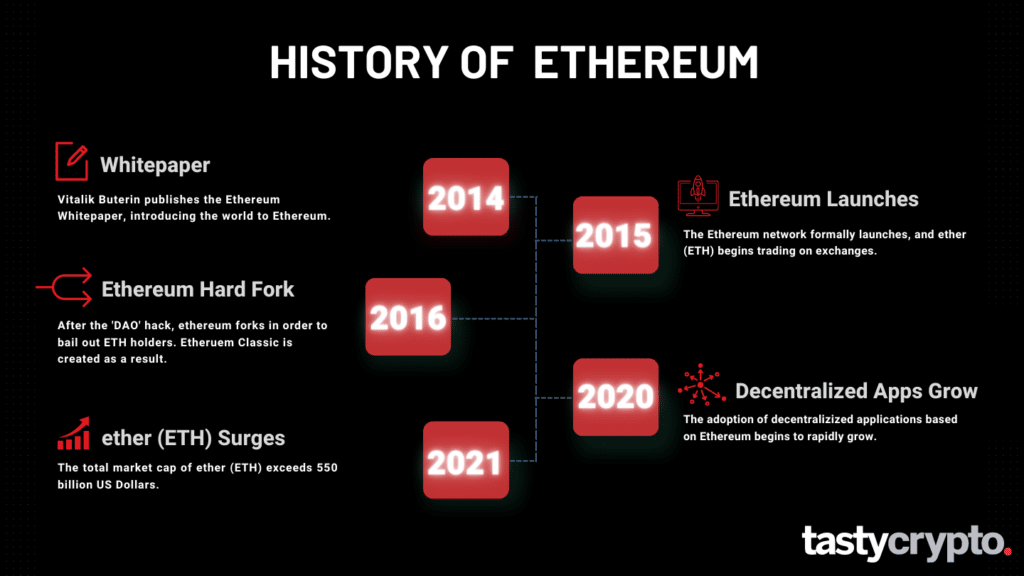
Ethereum was conceived by Vitalik Buterin in 2014 and launched in 2015.
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum is a proof-of-stake blockchain capable of executing smart contracts.
Smart contracts are like vending machines in that they are autonomous programs that rely on inputs and outputs.
Decentralized applications, or Web3 apps, are run on smart contracts.
Gas fees are the Ethereum network fees all users must pay to have their transactions added to the immutable Ethereum blockchain.
🚨 If you’re new to crypto, it may be helpful to read this guide first: What is Bitcoin and How Does It Work?
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is an open-source blockchain network that utilizes smart contract technology. The native cryptocurrency for the Ethereum network is ether (ETH), which is used as the blockchain’s medium of exchange. Ether is the second largest cryptocurrency in existence, second in market capitalization only to bitcoin (BTC).
Like all decentralized blockchain technologies, the Ethereum network is secured cryptographically. This security makes this peer-to-peer blockchain immutable, which means that once a transaction goes into a block, it can never be altered.
History of Ethereum
Nick Szabo creates ‘smart contracts’ in 1994.
Ethereum conceived in 2014 by Vitalik Buterin
Ethereum launched in 2015
The blockchain technology behind Ethereum was introduced to the world in 2014 by programmer Vitalik Buterin in his famous Ethereum Whitepaper. The actual network itself did not launch until 2015.
📚 Read! What Is a Whitepaper?
What made Ethereum a success was its ability to include smart contracts in its blocks.
“What Ethereum intends to provide is a blockchain with a built-in fully fledged Turing-complete programming language that can be used to create “contracts”.
Vitalik Buterin
Smart contracts, however, were not invented by Buterin. Nick Szabo create smart contracts back in 1994. Buterin ingeniously created a way to incorporate smart contracts into blockchain technology.
Vitalik Buterin Interview
tastylive interviewed Vitalik back in 2014! Check out the full interview below.
Ethereum vs Bitcoin

Bitcoin is a proof-of-work network; Ethereum is a proof-of-stake network
Ethereum can store smart contracts; Bitcoin can not
Ethereum is 99% more energy efficient than Bitcoin
The main difference between the Ethereum network (ETH) and the Bitcoin network (BTC) is what these blockchains are actually able to store.
Bitcoin can store only basic transactions in its blockchain. Ethereum, on the other hand, can store both transactions and code.
Ethereum’s ability to store code is due to the fact that this blockchain is “Turing complete”.
Turing complete (invented by Alan Turing in the mid-twentieth century) implies that a machine can, in theory, solve any computational problem. This allows the Ethereum network to use conditions and loops in order to program smart contracts.
Ethereum, therefore, can be used to create and recreate virtually any application that exists in the world of Web2, but in a decentralized Web3 ecosystem.
Since Bitcoin can not execute code, this blockchain is mainly used as a store of value, similar to digital gold.
📚 Read! Bitcoin is a Legit Store of Value. Here’s Why.
📕 Read! Bridges allow user to send ether to the Bitcoin network. Learn how bridges work here!
Proof-of-work vs Proof-of-Stake
Additionally, Bitcoin is a proof-of-work (PoW) network while Ethereum is a proof-of-stake (PoS) network. Proof-of-stake coins can be staked, allowing owners to earn interest on their coins similar to how one earns interest on cash in a bank account.
📖 Read! 5 Best Ways to Stake Your Ethereum
ETH vs BTC: Energy Consumption
In 2022, Ethereum switched its consensus mechanism from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake in an event called ‘The Merge’.
Proof-of-work networks are very expensive to operate. For this reason, Ethereum is about 99% more energy efficient than Bitcoin running under this new consensus mechanism.
How Ethereum Smart Contracts Work
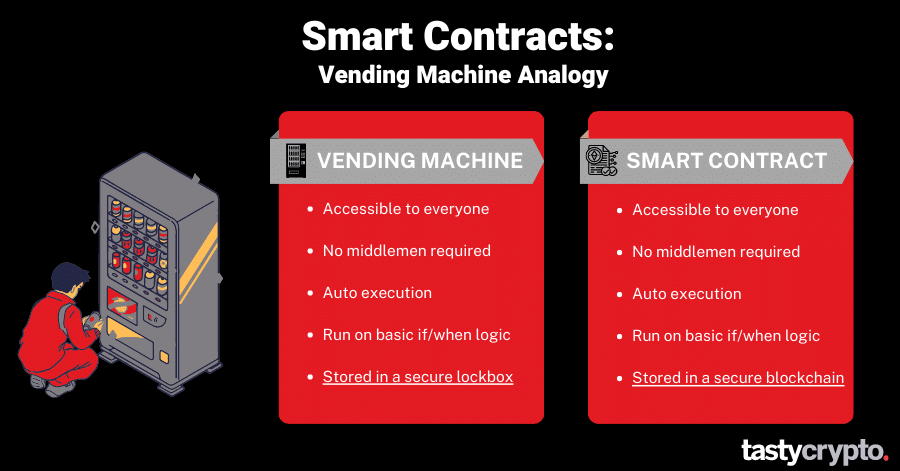
Though smart contracts can be a little intimidating to approach for newbies, they can be conceptually explained quite simply with the vending machine analogy.
A vending machine is autonomous. No third party is required for them to operate. Once an input is received ($3), an output is given (chips). While we are waiting for our chips to disperse, the machine safeguards the deposited coins and inventory.
A smart contract is also autonomous. Let’s look at a smart contract utilized in logistics for example.
If the GPS coordinates of a truck reach the delivery destination, then the driver will automatically be paid. In the meantime, a blockchain network will safeguard the funds and the integrity of the smart contract, only executing if and when this predetermined event occurs.
The main value-add of Ethereum smart contracts is that they eliminate the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts are particularly being embraced in finance and insurance as they make these traditionally paperwork-heavy industries much more efficient. In 2024, there are use cases for Ethereum in almost every major industry. See a few in the below article.
🍒 Go In-Depth: What Are Smart Contracts and How Do They Work?
Ethereum and dApps
When smart contracts are created with an interface, that interface is called a decentralized application, or a dApp.
dApps use smart contracts as their back end.
For example, let’s say you want to swap some ether (ETH) for some USDC on Uniswap, a popular decentralized exchange (DEX) dApp. USDC is a cryptocurrency stablecoin that tracks the price of the US Dollar fiat currency.
On the actual Uniswap interface, you will set this order up.
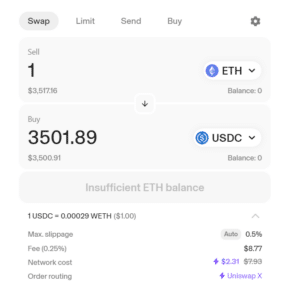
After you confirm the transaction in your self-custody cryptocurrency wallet, the Uniswap protocol will engage its liquidity pools which are stored on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Ethereum blockchain will then use its networks of ‘validators’ to add your transaction to the immutable blockchain. After the validators do their work, the entire Ethereum community will verify the transaction through the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. After this is complete (give it a few minutes) your transaction will be confirmed!
DeFi and Ethereum Explained
One of the fastest-growing segments of dApps is decentralized finance or DeFi.
Using smart contracts and sleek interfaces, DeFi is rebuilding finance in the decentralized space. This means that a community of users, rather than a traditional C-suite of executives, runs an organization.
There are DeFi protocols for all sorts of investing activities. Here are a few more popular DeFi activities:
Lending and borrowing
Crypto staking
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs): Trading
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs): Liquidity providing
Derivative trading
📚 Read more: DeFi Self-Custody Wallet FAQs
📚 Read More: 11 Best DeFi Crypto Coins for June 2024
Ethereum and Gas Fees
All users interacting with Ethereum must pay validators (nodes) for their work in adding transactions to a blockchain.
This fee is referred to as ‘gas’.
Gas fees are usually only a couple of dollars for simple transactions such as swapping crypto. The more complex your transaction, however, the more gas you will pay.
If you were to join a liquidity pool, for example, this will require more gas fees than a crypto swap because this involves multiple steps.
Launching smart contracts is a very computationally heavy task, and therefore costs a lot in gas fees. The most advanced smart contracts can cost thousands of dollars in gas fees to launch on Ethereum.
Ethereum gas fees are quoted in ‘gwei’, which represents 1/1,000,000,000 of 1 ETH.
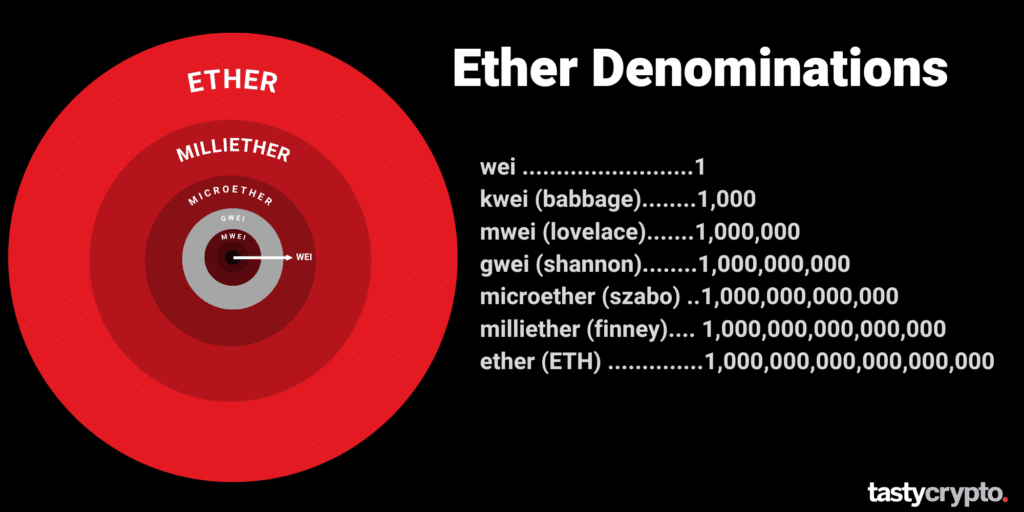
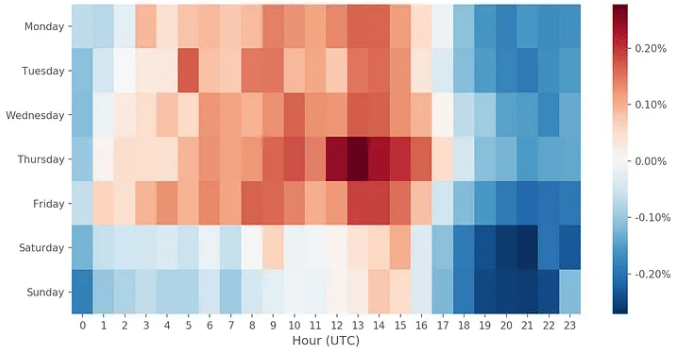
When Are ETH Gas Prices The Lowest?
The below chart shows us when gas fees are lowest.
How to Buy and Sell Ethereum
Cryptocurrency participants can trade ether (ETH) on both centralized exchanges and decentralized exchanges.
1. Buy and sell ether (ETH) on an exchange
A popular way to buy and sell ETH is through centralized exchanges, such as Coinbase, Gemini, Binance, and Kraken.
When you trade crypto on a centralized exchange, that exchange holds your private keys for you. This means there is no way for you to look your crypto up on a blockchain and guarantee that the exchange is indeed holding your crypto 1×1.
Trading crypto through a central authority is a lot simpler than trading crypto on a decentralized exchange via a self-custody wallet. If you forget or lose your password to a centralized exchange account, you can regain access to your digital assets through a simple password reset.
If you lose your self-custody seed phrase, however, there is no centralized party to restore it for you.
Read! Self-Custody Wallet FAQs
Another downside of trading crypto on a centralized exchange is the transaction fees, which can be very high.
2. Buy and sell ether (ETH) on a decentralized exchange
Trading ether on a decentralized exchange (DEX) is often much cheaper than trading ether on a centralized exchange. In addition to this cost-efficiency, when you own ether in a self-custody wallet, you can guarantee that your digital assets are not being lent out or traded upon (a major problem with centralized exchanges like FTX).
In order to trade ether on a DEX, you will first need a self-custody wallet.
Check out the tastycrypto self-custody wallet here!
To trade ether with a self-custody wallet, you must first assure that your selected wallet is an ‘Ethereum wallet’. Some wallets only interact with one blockchain while others interact with many. The tastycrypto wallet is compatible with the Ethereum network.
Just as with centralized exchanges, however, self-custody wallets are vulnerable to hacks. It is therefore important to follow these guidelines when using a self-custody wallet.
📚 Read! Self-Custody vs Custodial Wallets
For those new to cryptocurrency, this post from investor.gov may help in navigating the risks involved.
FAQs
Ethereum Classic is an open-source blockchain network. Ethereum classic launched in 2016 as a result of a hard fork. The fork followed a major hack of an application called the DAO that ran on the Ethereum blockchain.
In 2022, the Ethereum network changed its consensus mechanism from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake in an event called The Merge. This has opened the door to ‘sharding’, which will increase transaction throughput and lower Ethereum gas fees later in 2024.
All Ethereum tokens are created using the ERC-20 standard. Ethereum itself, however, is not an ERC-20 token. Therefore, in order to use Ethereum on decentralized applications, users must use wrapped Ethereum or wETH. wETH tracks the price of Ethereum.

Mike Martin
Mike Martin formerly served as the Head of Content for tastycrypto. Before joining tastycrypto, Michael worked in the active trader divisions of thinkorswim, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. He also served as a writer and editor for projectfinance.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads


Crypto Burning Guide: What It Means and How It Works

Crypto Coin vs Token: What’s The Difference?
Leverage in Crypto Trading: 6 Key Examples

What Is Slippage in Crypto? Beginners Guide